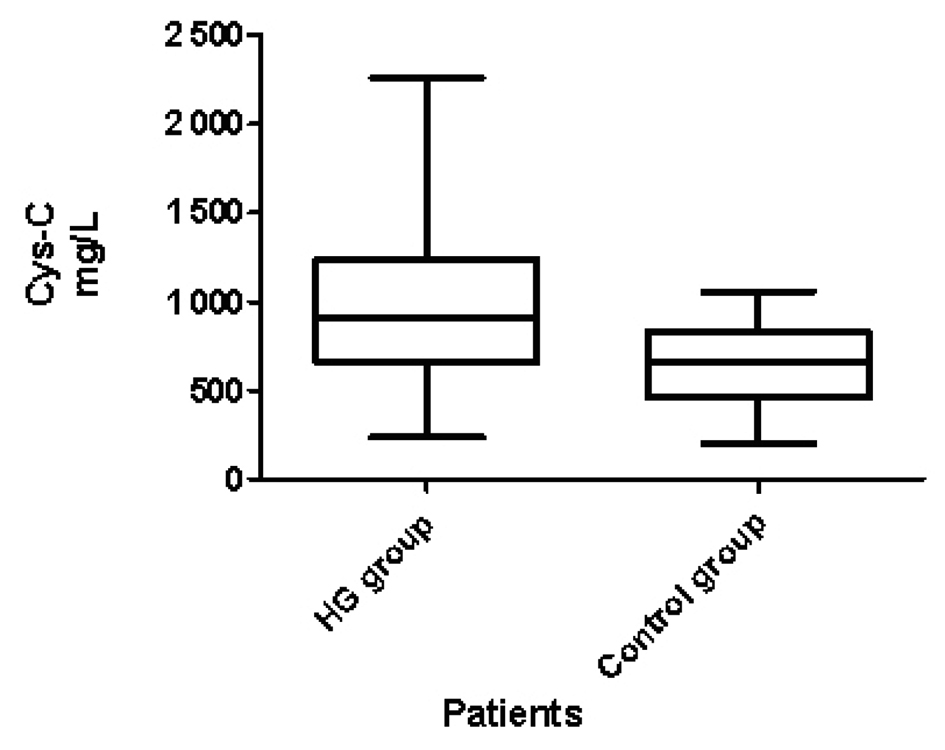
Figure 1. Cys-C levels in HG and controls.
| Journal of Clinical Gynecology and Obstetrics, ISSN 1927-1271 print, 1927-128X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Gynecol Obstet and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jcgo.org |
Original Article
Volume 1, Number 1, February 2012, pages 10-14
Increased Cys-C Levels in Hyperemesis Gravidarum
Figure

Table
| Patients (n = 37) | Controls (n = 33) | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Values are expressed as mean 8 SD or median (interquartile range). Hgb: Hemoglobuline; Plt:Thrombocyte; BUN: Blood urea nitrogen; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; TSH: Thyroid stimulating hormone; Cys-C: Cystatin C. | |||
| Age, years | 25.4 ± 5.2 | 25.3 ± 4.5 | 0.36 |
| Gestation, week | 9.7 ± 2.2 | 10 ± 2.2 | 0.73 |
| Weight, kg | 63 ± 11 | 62 ± 9 | 0.34 |
| Creatine | 0.65 ± 0.1 | 0.61 ± 0.1 | 0.74 |
| Hgb.g/dL | 12 ± 0.9 | 11.7 ± 1 | 0.33 |
| Plt. ×103µL | 234 ± 67 | 226 ± 48 | 0.056 |
| Glucose, mg/dL | 85 ± 8 | 86 ± 8 | 0.75 |
| BUN, mg/100 ml | 20 ± 6.3 | 16 ± 3.3 | 0.005 |
| AST, u/L | 18 ± 7.5 | 17 ± 3 | 0.01 |
| ALT, u/L | 18 ± 14 | 14 ± 4 | 0.04 |
| Sodium, mEq/L | 135 ± 2.7 | 136 ± 1.7 | 0.005 |
| Potasium, mEq/L | 3.9 ± 0.3 | 3.6 ± 0.3 | 0.9 |
| TSH, mIU/l | 0.95 ± 0.56 | 1.4 ± 1.15 | 0.03 |
| Cys-C | 1.007 ± 0.7 | 0.635 ± 0.4 | 0.0002 |