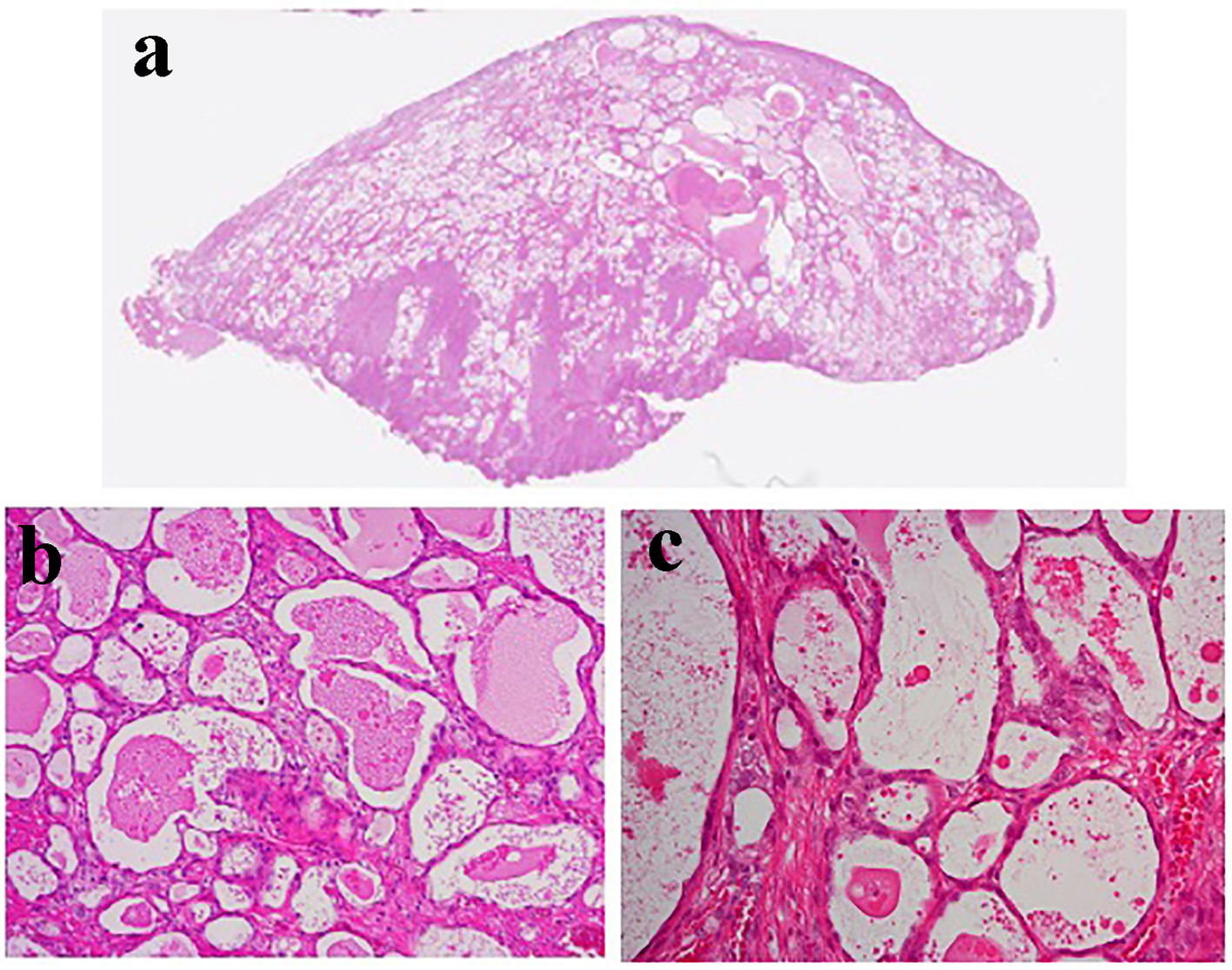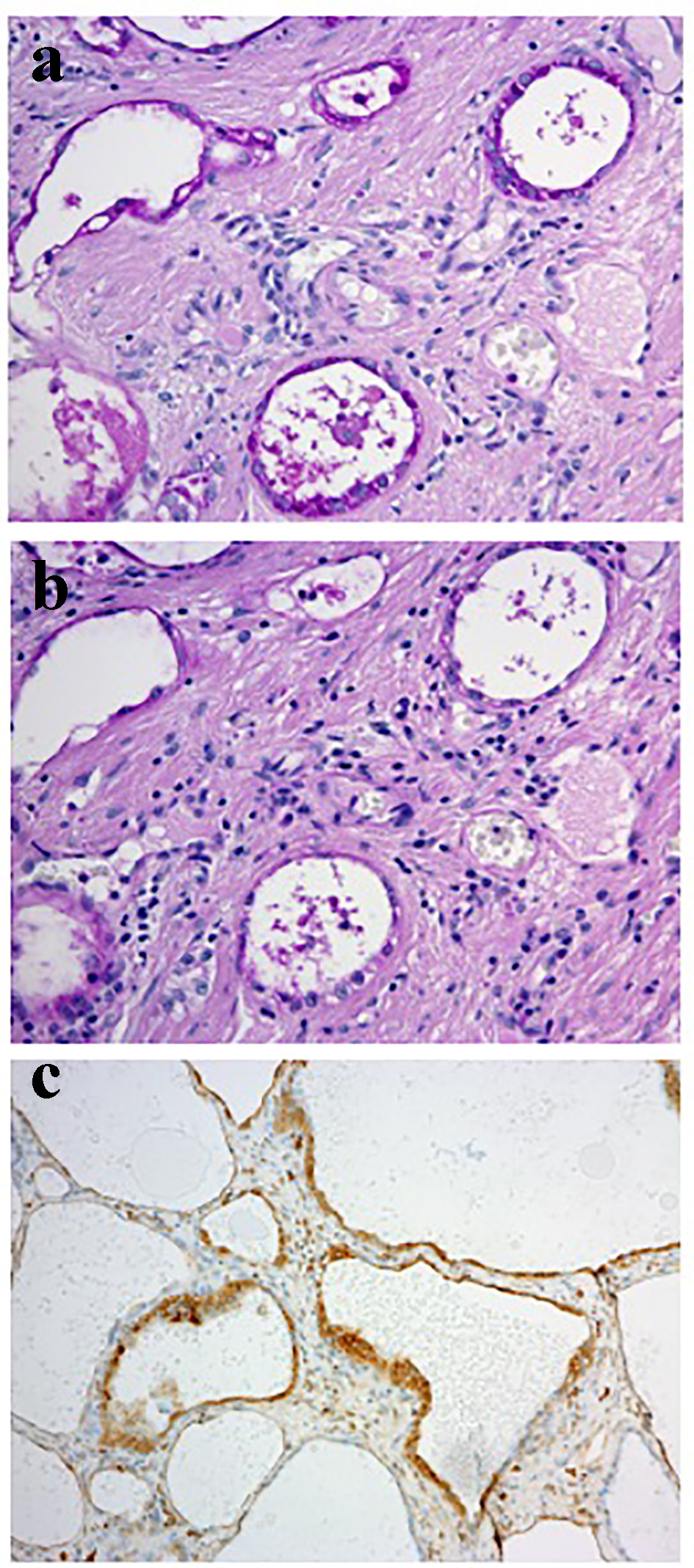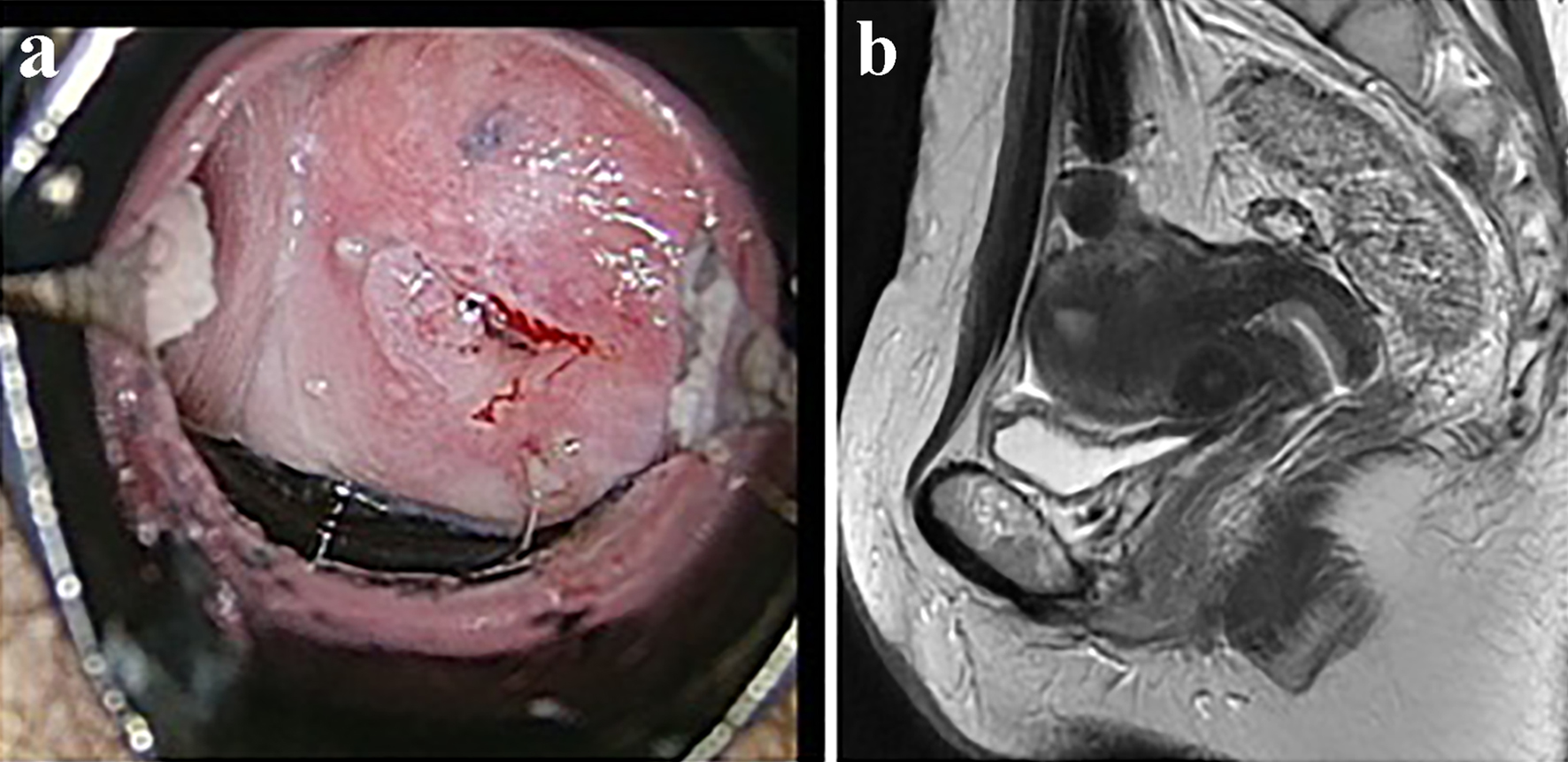
Figure 1. The results of imaging examinations. (a) Colposcopic findings. Atypical vessels were detected on colposcopy. (b) T2-weighted pelvic MRI images. No tumor was detected.
| Journal of Clinical Gynecology and Obstetrics, ISSN 1927-1271 print, 1927-128X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Gynecol Obstet and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jcgo.org |
Case Report
Volume 8, Number 1, March 2019, pages 21-24
Annual Cervical Cancer Screening Revealed Early Stage Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma of the Uterine Cervix: A Case Report
Figures