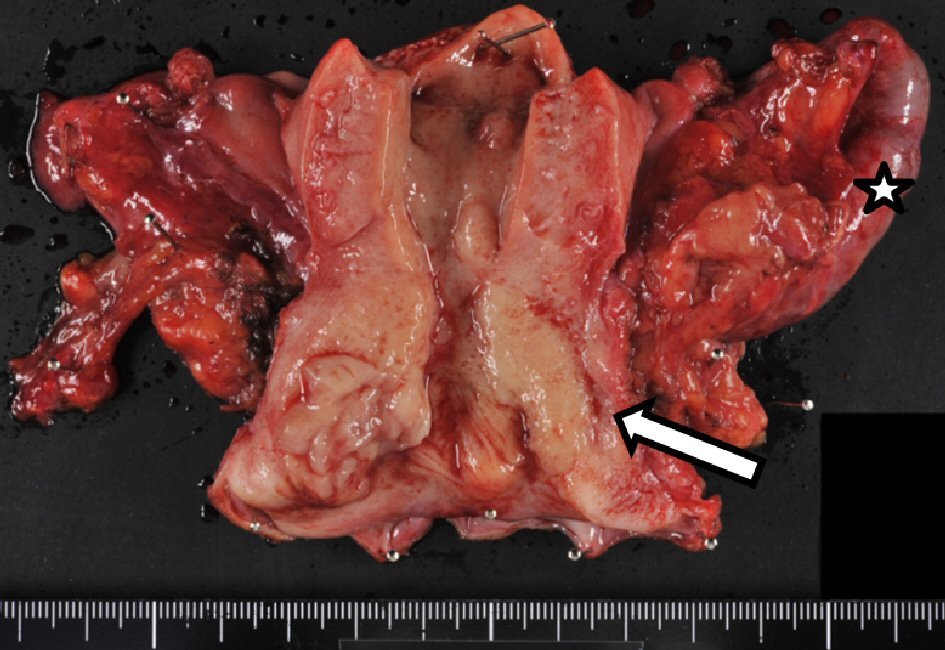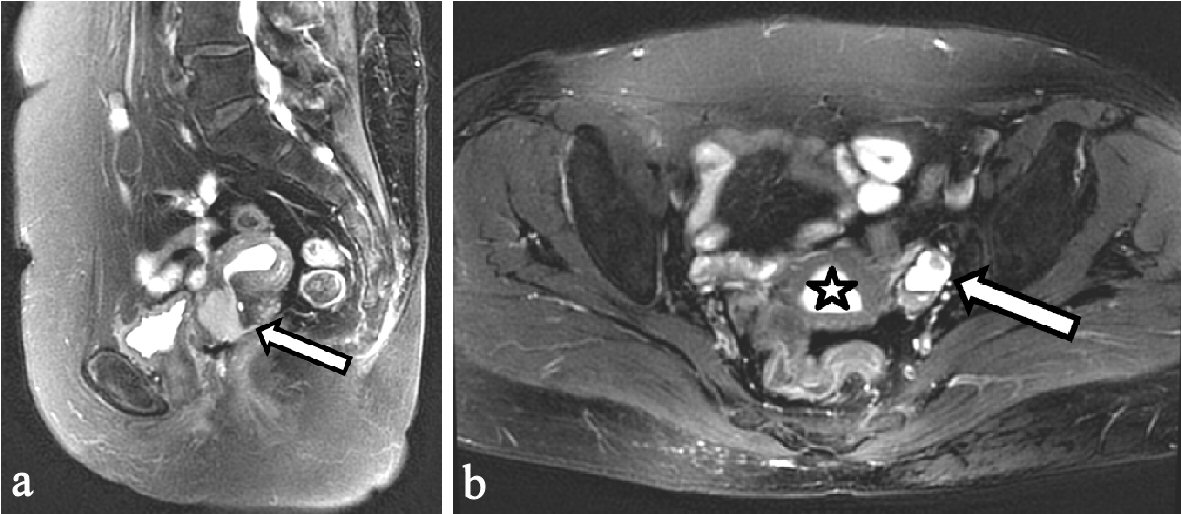
Figure 1. Preoperative pelvic MRI. (a) Sagittal T2-weighted imaging. A 24-mm cervical tumor showing high-intensity signal (arrow). (b) Axial T2-weighted imaging, hematometra (asterisk) and left hematosalpinx with mural nodule (arrow) showing high-intensity signal. MRI: magnetic resonance imaging.
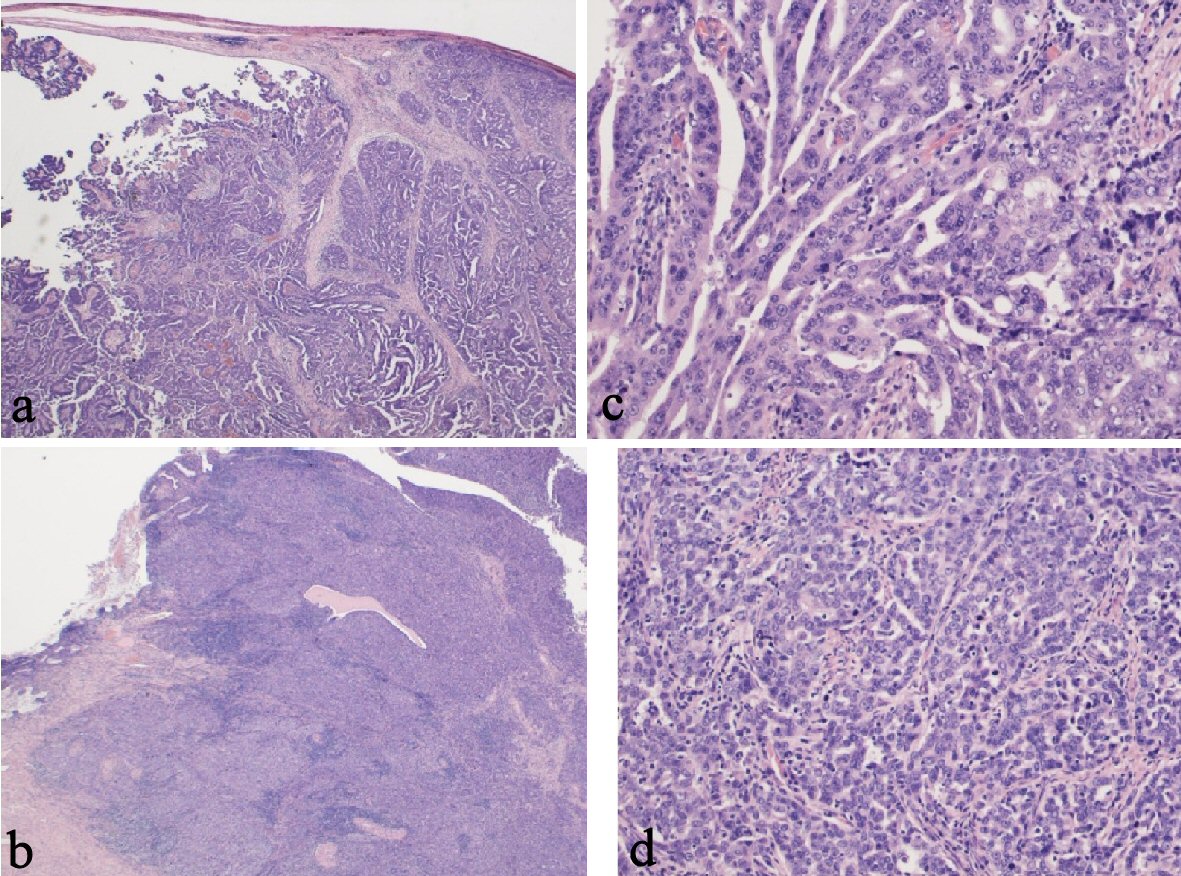
Figure 3. Pathological findings. (a) Left fallopian tube, carcinoma with infiltration into the tubal wall (H&E staining, × 15). (b) Left fallopian tube, papillary serous adenocarcinoma (H&E staining, × 150). (c) Cervix, carcinoma and remaining cervical glands (H&E staining, × 15). (d) Cervix, serous adenocarcinoma similar to a fallopian tube carcinoma (H&E staining, × 150). H&E: hematoxylin and eosin stain.