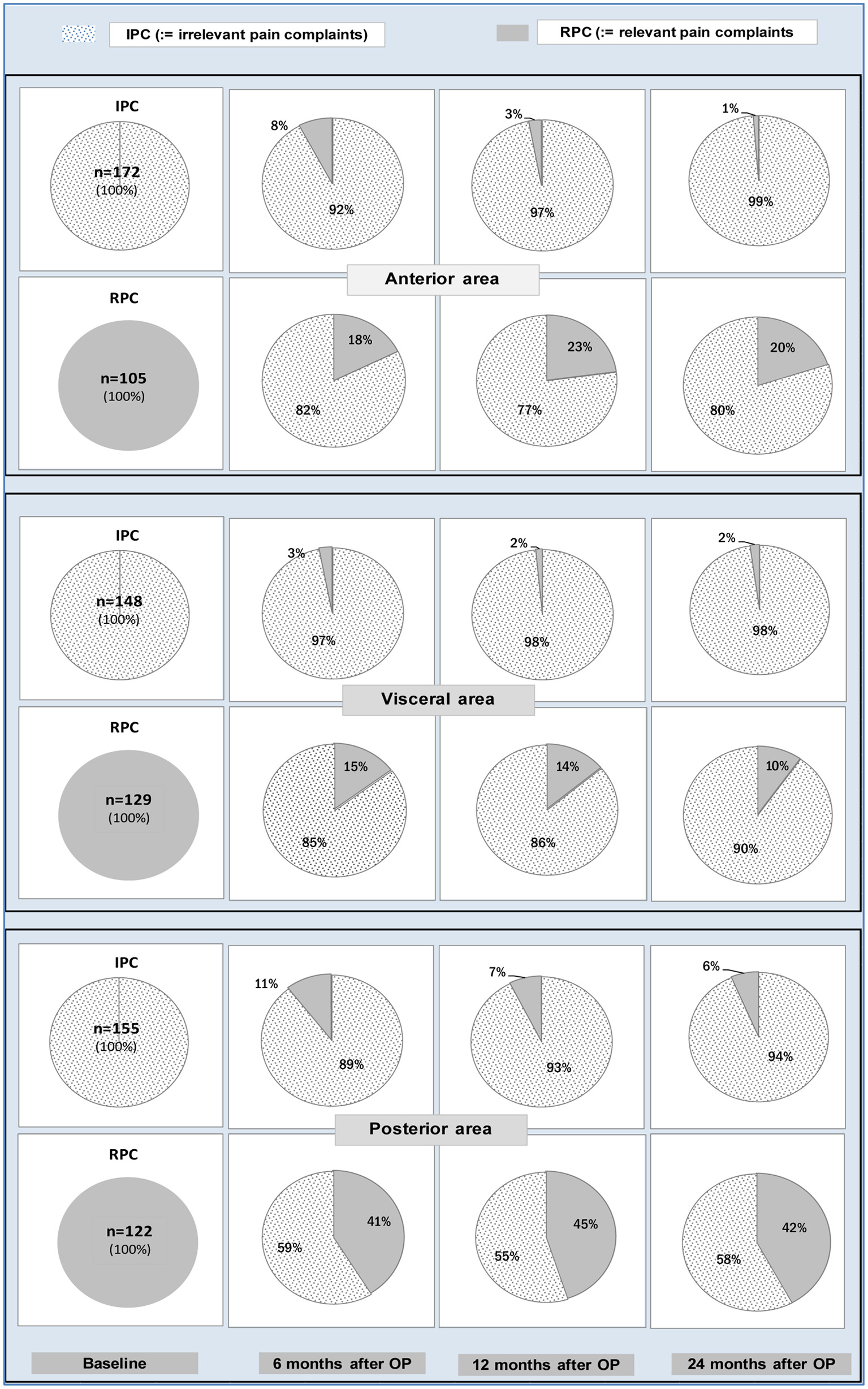
| Front area (PFDI 1 and PFDI 2) (RPC: “PFDI 1 = R2 or PFDI 2 = R2”) | | | | | | | | | | |
| RPC in the “POP-Q stage 2” sample | 48 | 39.30% | 13 | 11.60% | 16 | 14.30% | 9 | 9.90% | Q(DF = 3) = 49.25 | 0/1, 0/2, 0/3 |
| Total cases | 122 | | 112 | | 112 | | 91 | | P < 0.00001* | |
| RPC in the “POP-Q stage 3/4” sample | 55 | 36.70% | 17 | 12.10% | 6 | 4.60% | 2 | 2.20% | Q(DF = 3) = 86.28 | 0/1, 0/2, 0/3 |
| Total cases | 150 | | 140 | | 131 | | 89 | | P < 0.00001* | |
| X2-tests for testing POP-Q stage 2 vs. POP-Q stage 3 or 4 | X2(1) = 0.20
P = 0.650 | | X2(1) = 0.02
P = 0.896 | | X2(1) = 6.90
P = 0.008* | | X2(1) = 4.58
P = 0.032+ | | | |
| Visceral area (PFDI 3 and PFDI 6) (RPC: “PFDI 3 = R2 or PFDI 6 = R2”) | | | | | | | | | | |
| RPC in the “POP-Q stage 2” sample | 53 | 43.40% | 13 | 11.60% | 12 | 10.70% | 8 | 8.80% | Q(DF = 3) = 65.26 | 0/1, 0/2, 0/3 |
| Total cases | 122 | | 112 | | 112 | | 91 | | P < 0.00001* | |
| RPC in the “POP-Q stage 3/4” sample | 74 | 49.30% | 9 | 6.40% | 6 | 4.60% | 3 | 3.40% | Q(DF = 3) = 124.70 | 0/1, 0/2, 0/3 |
| Total cases | 150 | | 140 | | 131 | | 89 | | P < 0.00001* | |
| X2-tests for testing POP-Q stage 2 vs. POP-Q stage 3 or 4 | X2(1) = 0.93
P = 0.332 | | X2(1) = 2.09
P = 0.146 | | X2(1) = 3.31
P = 0.068 | | X2(1) = 2.30
P = 0.129 | | | |
| Posterior area (PFDI 7 and PFDI 46) (RPC: “PFDI 7 = R2 or PFDI 46 = R2”) | | | | | | | | | | |
| RPC in the “POP-Q stage 2” sample | 55 | 43.40% | 32 | 28.60% | 36 | 32.10% | 27 | 29.70% | Q(DF = 3) = 11.24 | 0/1, 0/2+, 0/3+ |
| Total cases | 122 | | 112 | | 112 | | 91 | | P = 0.0105+ | |
| RPC in the “POP-Q stage 3/4” sample | 74 | 49.30% | 30 | 21.40% | 20 | 15.30% | 12 | 13.50% | Q(DF = 3) = 25.96 | 0/1, 0/2, 0/3 |
| Total cases | 150 | | 140 | | 131 | | 89 | | P < 0.00001* | |
| X2-tests for testing POP-Q stage 2 vs. POP-Q stage 3 or 4 | X2(1) = 0.08
P = 0.772 | | X2(1) = 1.71
P = 0.190 | | X2(1) = 9.69
P = 0.002* | | X2(1) = 6.94
P = 0.008* | | | |
| All areas (PFDI: 1, 2, 3, 6, 7 and 46) (RPC: “at least one of the PFDIs = R2”) | | | | | | | | | | |
| RPC in the “POP-Q stage 2” sample | 55 | 45.10% | 39 | 34.80% | 44 | 39.30% | 32 | 35.20% | Q(DF = 3) = 39.64 | 0/1, 0/2, 0/3 |
| Total cases | 122 | | 112 | | 112 | | 91 | | P < 0.00001* | |
| RPC in the “POP-Q stage 3/4” sample | 65 | 43.30% | 41 | 29.30% | 22 | 16.80% | 14 | 15.70% | Q(DF = 3) = 81.38 | 0/1, 0/2, 0/3 |
| Total cases | 150 | | 140 | | 131 | | 89 | | P < 0.00001* | |
| X2-tests for testing POP-Q stage 2 vs. POP-Q stage 3 or 4 | X2(1) = 1.41
P = 0.559 | | X2(1) = 0.87
P = 0.348 | | X2(1) = 15.43
P < 0.0001* | | X2(1) = 8.93
P = 0.002* | | | |