| Journal of Clinical Gynecology and Obstetrics, ISSN 1927-1271 print, 1927-128X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Gynecol Obstet and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jcgo.org |
Case Report
Volume 7, Number 1, March 2018, pages 20-22
Chemical Inflammation Associated With Adhesion Barrier Following Cesarean Section
Asako Nagashimaa, Shunji Suzukia, b
aDepartment of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Japanese Red Cross Katsushika Maternity Hospital, Tokyo, Japan
bCorresponding Author: Shunji Suzuki, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Japanese Red Cross Katsushika Maternity Hospital, 5-11-12 Tateishi, Katsushika-ku, Tokyo 124-0012, Japan
Manuscript submitted December 12, 2017, accepted February 21, 2018
Short title: Chemical Inflammation With Adhesion Barrier
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/jcgo472e
| Abstract | ▴Top |
A 24-years-old woman (gravid 1, para 0) underwent an emergency cesarean section (CS) at 41 weeks of gestation. Seven days after CS, a low-density area of 55 × 40 mm having a high-density well-defined border indicating capsulized fluid was observed in front of the uterine anterior wall by ultrasonography. There was slightly tenderness and rebound tenderness in this part. At this time, the patient had awareness of frequent urination without fever or pain, and her white blood cell count was increased. Ten days after CS, she developed fever with micturition pain, while there was no abnormality in her urine sediment. Based on these findings, we diagnosed it as chemical inflammation associated with adhesion barrier.
Keywords: Chemical inflammation; Adhesion barrier; Ultrasonography
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Mechanical bioresorbable adhesion barrier has been applied to adhesiogenic tissues before surgical closure. It is indicated for the reduction in the incidence, extent, and severity of postoperative adhesions in patients undergoing abdominal or pelvic laparotomy. To date, some cases of chemical peritonitis (inflammation) associated with adhesion barrier following gastroenterological surgery have been reported [1-4]. We present here a case of chemical inflammation associated with adhesion barrier following emergency cesarean section (CS).
| Case Report | ▴Top |
A 24-years-old woman, gravid 1, para 0 with no previous disease or family history underwent an emergency CS at 41 weeks of gestation because of fetal asphyxia. A female infant weighing 3,430 g was born with Apgar scores of 9 and 9 at 1 and 5 min, respectively. Four sheets of adhesion barrier (Seprafilm®) were placed in front of the uterine anterior wall as shown in Figure 1. At this time, her white blood cell count (WBC) and C-reactive protein (CRP) were 9,560/mm3 and 0.85 mg/dL, respectively. Histopathology of the placenta did not demonstrate any abnormal findings except acute chorioamnionitis. Total blood loss during surgery was 500 mL. Flomoxef sodium®, which is a cephem-based antibiotics showing antimicrobial activity mainly with aerobic bacteria, had been used for 3 days to prevent postoperative intrauterine infection. The clinical course until 6 days after CS was uneventful without any further complications.
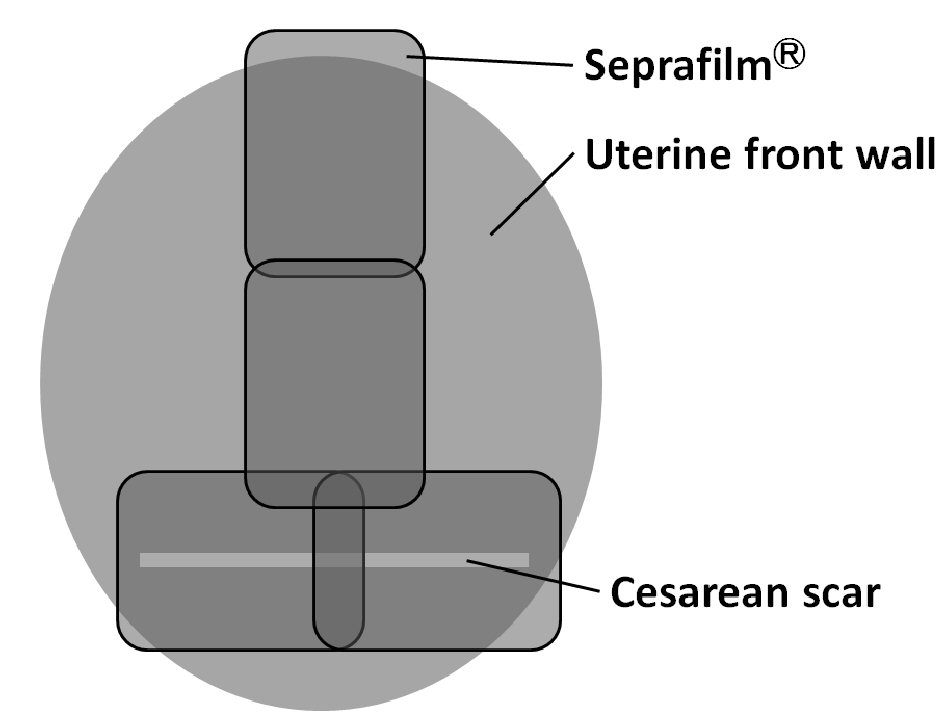 Click for large image | Figure 1. Four sheets of adhesion barrier (Seprafilm®) were placed in front of the uterine anterior wall. |
Seven days after CS, a low-density area of 55 × 40 mm having a high-density well-defined border indicating capsulized fluid was observed in front of the uterine anterior wall by ultrasonography (Fig. 2) which is our routine examination to permit discharge from the hospital. This position was different from that of the CS scar. There was slightly tenderness and rebound tenderness in this part. At this time, the patient had awareness of frequent urination without fever or pain, and her WBC was 11,100/mm3. Ten days after CS, she developed fever (38 °C) with micturition pain although the tenderness and rebound tenderness had decreased. The appearance of her urine was clear, and there was no abnormality in her urine sediment. Based on these findings, we diagnosed it as chemical inflammation associated with adhesion barrier.
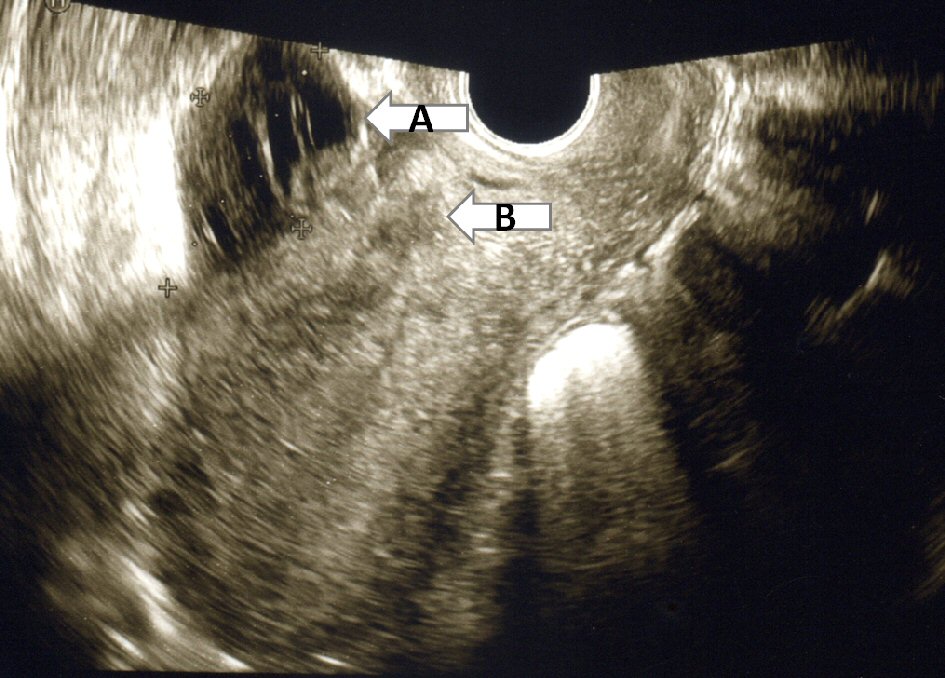 Click for large image | Figure 2. A low-density area of 55 × 40 mm having a high-density well-defined border indicating capsulized fluid (arrow A) was observed in front of the uterine anterior wall by ultrasonography. The position was different from that of the cesarean section scar (arrow B). |
Clindamycin was used to prevent anaerobic bacterial infection. Seventeen days after CS, her frequent urine, micturition pain and fever disappeared. The tenderness and rebound tenderness disappeared. The low-density area having a high-density well-defined border was decreased as shown in Figure 3. In addition, her WBC and CRP decreased to 8,770/mm3 and 2.77, respectively. Twenty-seven days after CS, the size of low-density area having a high-density well-defined border was decreased significantly as shown in Figure 4.
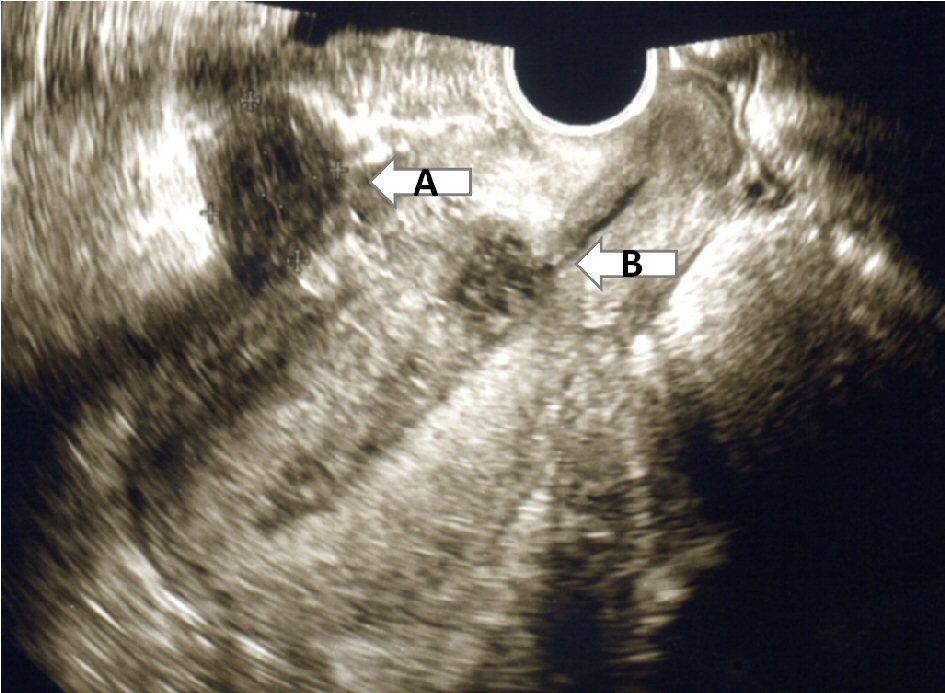 Click for large image | Figure 3. A low-density area having a high-density well-defined border (arrow A) was observed in front of the uterine anterior wall by ultrasonography. The position was different from that of the cesarean section scar (arrow B). |
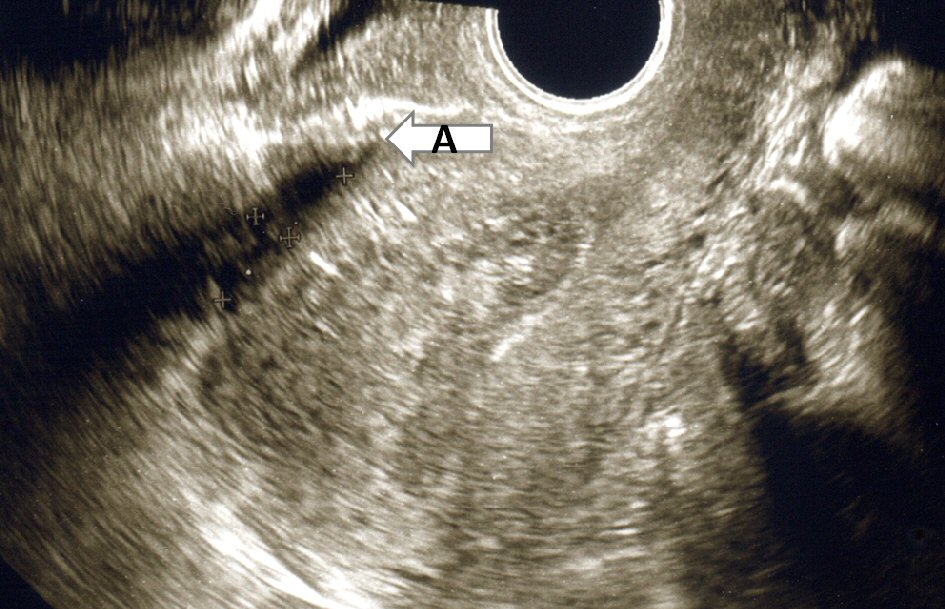 Click for large image | Figure 4. The size of low-density area having a high-density well-defined border was (arrow A) decreased significantly. |
Number of cases of chemical inflammation associated with adhesion barrier following CS
In our institute, we have used two types of adhesion barrier. One is Seprafilm®, which is comprised of two anionic polysaccharides: modified hyaluronic acid and carboxymethylcellulose, and the other is Gynecare Interceed®, which is a fabric composed of oxidized, regenerated cellulose [5-7].
To date, we have encountered four cases of chemical inflammation associated with adhesion barrier following CS. Seprafilm® was associated with two cases (per 612 cases, 0.33%), while Gynecare Interceed® was associated with the other two cases (per 1252 cases, 0.16%, P = 0.84 by the X2 test with correction of Yates, unpublished data).
| Discussion | ▴Top |
There have been few case reports of chemical inflammation following CS associated with adhesion barrier; however, there have been some case reports showing serious clinical peritonitis induced by adhesion barrier following gastroenterological surgery [1-4]. In these previous cases [1-4], clinical findings of intra-abdominal inflammatory reaction were observed in 4 to 13 days after the operation. In the cases reported previously, developed fever (> 30 °C), increased WBC and the physical examination revealing tenderness and rebound tenderness were observed. In these cases [1-4], the diagnosis of chemical peritonitis were done based on the findings of intense of intra-abdominal inflammatory reaction in the abdominal cavity and negative finding of postoperative culture of ascites at the second laparotomy. In this case, we did not perform the laparotomy; however, we diagnosed it as chemical inflammation based on the clinical courses with the presences of capsulized fluid in the part of adhesion barrier application distant from the CS scar. In the previous cases [1-4], the presences of capsulized fluid have been detected by computed tomography (CT); however, we used ultrasound examination, which has been used routinely by obstetricians, to confirm the diagnosis chemical inflammation in this case. Therefore, this may be the first case report showing the ultrasonographic findings of chemical inflammation associated with adhesion barrier.
The mechanisms leading to chemical inflammation associated with adhesion barrier have not been clear. In our institute, we have used two types of adhesion barrier (Seprafilm® and Gynecare Interceed®) as previously mentioned. Chemical inflammation may occur at low frequency using either types of adhesion barrier. To date, adhesion barrier itself has not been reported to adversely affect postoperative inflammatory response based on the serum inflammatory cytokine levels or clinical outcomes even in patients with intraperitoneal septic complications [8]. In an earlier case of chemical peritonitis following abdominal surgery by Kobayashi et al [1], an intense foreign body reaction composed of macrophages was identified in the site of adhesion barrier application, which is the end-stage response of the inflammatory and wound healing responses following implantation of a medical device, prosthesis, or biomaterial [9]. In the cases with the chemical inflammation, the patients may have abnormalities in immune reaction against adhesion barrier. In addition, the hyaluronan-based membrane has been observed to be associated with an increased adhesion in an animal model of bacterial peritonitis [10, 11]. Therefore, surgeons must be cautions of using adhesion barrier in patients with bacterial peritonitis even if abdominal lavage was extensively performed. In case of emergency CS especially after rupture of the membranes and/or intrauterine infection, we may have to consider the possibility of bacterial peritonitis.
Conclusions
A case of chemical inflammation associated with adhesion barrier following emergency CS was presented. We diagnosed it as chemical inflammation based on the clinical courses with the presences of capsulized fluid in the part of adhesion barrier application distant from the CS scar.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest relevant to this article.
| References | ▴Top |
- Kobayashi K, Watanabe M, Ushigome T, Aoki H, Shida A, Yanaga K. Chemical peritonitis induced by an anti adhesion bioresorbable membrane : a case report and review of the literatures. Jikeikai Med J. 2006;53(4):161-175.
- Klingler PJ, Floch NR, Seelig MH, Branton SA, Wolfe JT, Metzger PP. Seprafilm-induced peritoneal inflammation: a previously unknown complication. Report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 1999;42(12):1639-1643.
doi pubmed - Wagatsuma S, Yokoyama T, Sakurada S, Matsumoto H, Hoshiai T. A case of chemical peritonitis induced by an anti adhesion bioresorbable membrane (Seprafilm®) (in Japanese). Obstet Gynecol Ptactice. 2014;63(1):133-137.
- Kawamura S, Ishikawa T. An unfixed form case of intra-abdominal abscess following operation (in Japanese). J Iwate Perfect Hosp Assoc. 2006;46(1):49-54.
- Kayaoglu HA, Ozkan N, Hazinedaroglu SM, Ersoy OF, Koseoglu RD. An assessment of the effects of two types of bioresorbable barriers to prevent postoperative intra-abdominal adhesions in rats. Surg Today. 2005;35(11):946-950.
doi pubmed - Seprafilm® Adhesion Barrier Official Site: https://www.seprafilm.us/ (Dec 3, 2017).
- GYNECARE INTERCEED® Absorbable Adhesion Barrier Official Site: http://www.ethicon.com/ (Dec 2, 2017).
- Uchida K, Urata H, Mohri Y, Inoue M, Miki C, Kusunoki M. Seprafilm does not aggravate intraperitoneal septic conditions or evoke systemic inflammatory response. Surg Today. 2005;35(12):1054-1059.
doi pubmed - Anderson JM, Rodriguez A, Chang DT. Foreign body reaction to biomaterials. Semin Immunol. 2008;20(2):86-100.
doi pubmed - Ghellai AM, Stucchi AF, Lynch DJ, Skinner KC, Colt MJ, Becker JM. Role of a hyaluronate-based membrane in the prevention of peritonitis-induced adhesions. J Gastrointest Surg. 2000;4(3):310-315.
doi - Tzianabos AO, Cisneros RL, Gershkovich J, Johnson J, Miller RJ, Burns JW, Onderdonk AB. Effect of surgical adhesion reduction devices on the propagation of experimental intra-abdominal infection. Arch Surg. 1999;134(11):1254-1259.
doi pubmed
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Clinical Gynecology and Obstetrics is published by Elmer Press Inc.
