| Journal of Clinical Gynecology and Obstetrics, ISSN 1927-1271 print, 1927-128X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Gynecol Obstet and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.jcgo.org |
Case Report
Volume 9, Number 3, September 2020, pages 70-72
Ruptured Heterotopic Pregnancy Following Spontaneous Conception
Alexandra Samborskia, b, Chloe Williamsa, Lauren E. Spivacka, Ashley L. Gubbelsa
aDepartment of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, NY, USA
bCorresponding Author: Alexandra Samborski, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Rochester Medical Center, 601 Elmwood Avenue, Box 668, Rochester, NY, USA
Manuscript submitted July 16, 2020, accepted July 23, 2020, published online September 9, 2020
Short title: Ruptured Heterotopic Pregnancy
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/jcgo673
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Heterotopic pregnancy following natural conception cycles is a rare event, estimated at one in 30,000 pregnancies. This infrequent phenomenon leads to significant morbidity and potential mortality if not promptly diagnosed. We present the case of a 29-year-old with no identifiable risk factors who presented with hemoperitoneum and hypotension. The patient had a visualized intrauterine pregnancy (IUP) and a marked amount of free fluid on transvaginal ultrasound. At the time of diagnostic laparoscopy, a ruptured left tubal pregnancy was identified. This case highlights that diagnosis of an IUP does not exclude a simultaneous heterotopic pregnancy even in patients for whom no identifiable risks factors can be found. Similarly, diagnosis of an IUP should not lead to delay in treatment of hemoperitoneum.
Keywords: Heterotopic pregnancy; Ectopic pregnancy; Hemoperitoneum; Intrauterine pregnancy
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Heterotopic pregnancy, or implantation of pregnancies in more than one location, is a rare diagnosis, but carries a high risk of morbidity and mortality if not promptly diagnosed. Heterotopic pregnancies have been reported as early as 1708 in a post-mortem case report of a patient who died secondary to a ruptured ectopic pregnancy [1]. Given the rarity of heterotopic pregnancy in the absence of assisted reproductive technology (ART), this diagnosis may often be overlooked in favor of more common diagnoses. Although it is difficult to calculate the exact incidence of heterotopic pregnancy, the theoretical risk for spontaneous heterotopic pregnancy is one in 30,000, calculated using the rate of fraternal twins (one in 110) and the rate of spontaneous ectopic pregnancy (one in 250) [2]. This risk increases with use of ART and has been estimated to be as high as one in 100 in pregnancies conceived in this manner [1, 3, 4]. Typically, these pregnancies are diagnosed between 5- and 8-week gestational age (70%), with only a small minority of cases diagnosed after 11-week gestation (10%). The rarity of the presentation for patients with no history of ART may lead to misdiagnosis in patients presenting with hemoperitoneum and an identified intrauterine pregnancy (IUP). However, the high potential for significant morbidity and mortality obligates clinicians to consider and diagnose heterotopic pregnancies promptly.
| Case Report | ▴Top |
A 29-year-old G3P0020 female with a history of depression, anxiety, palpitations, and asthma presented to the emergency department (ED) with acute worsening abdominal pain over the last 3 days, in addition to associated nausea, vomiting, and a pre-syncopal episode. She was sexually active without contraception. She reported that she recently had a positive pregnancy test and was scheduled for a termination the following week as this was an undesired pregnancy. She started having vaginal bleeding shortly prior to her presentation to the ED. Upon initial evaluation, she reported that her symptoms felt similar to previous episodes of syncope which had resulted in a normal cardiology workup.
On initial presentation, her vital signs were significant for tachycardia to the 140s. She was initially normotensive, but subsequently developed hypotension responsive to intravenous (IV) fluids. Initial hemoglobin was 6.7 and her beta human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) was 92,641. A focused assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST) exam performed by the ED providers revealed significant free fluid in the pelvis and in the right upper quadrant. A transvaginal ultrasound revealed an IUP measuring 7-week and 4-day gestation with cardiac activity, which was consistent with her last menstrual period. It additionally showed a marked amount of free fluid in the pelvis. The right ovary appeared to have either a cyst or surrounding clot, although visualization was limited. The left ovary was visualized and appeared normal. Her abdominal exam was notable for increased tenderness with rebound and guarding. She denied a history of prior ectopic pregnancy, tubal surgeries, pelvic inflammatory disease or abdominal surgery. She was a current tobacco user.
The leading diagnosis at this time was a ruptured ovarian cyst, presumably a corpus luteal cyst, with ongoing intraabdominal bleeding. The patient confirmed that the pregnancy was undesired, thus the decision was made to proceed urgently to the operating room for diagnostic laparoscopy as well as dilation and evacuation for termination of the IUP. Laparoscopy revealed 1.2 L of blood in the abdomen, a right paratubal cyst, and a left ruptured tubal ectopic pregnancy (Fig. 1). The patient underwent laparoscopic evacuation of hemoperitoneum, left salpingectomy, right paratubal cystectomy, and therapeutic dilation and evacuation (Fig. 2). She received one unit packed red blood cells due to symptomatic anemia. She was discharged home on postoperative day 0 in stable condition. Pathology confirmed the suspected diagnosis of heterotopic pregnancy with intrauterine products of conception and left fallopian tube with focal implantation site and rare chorionic villi consistent with ectopic pregnancy.
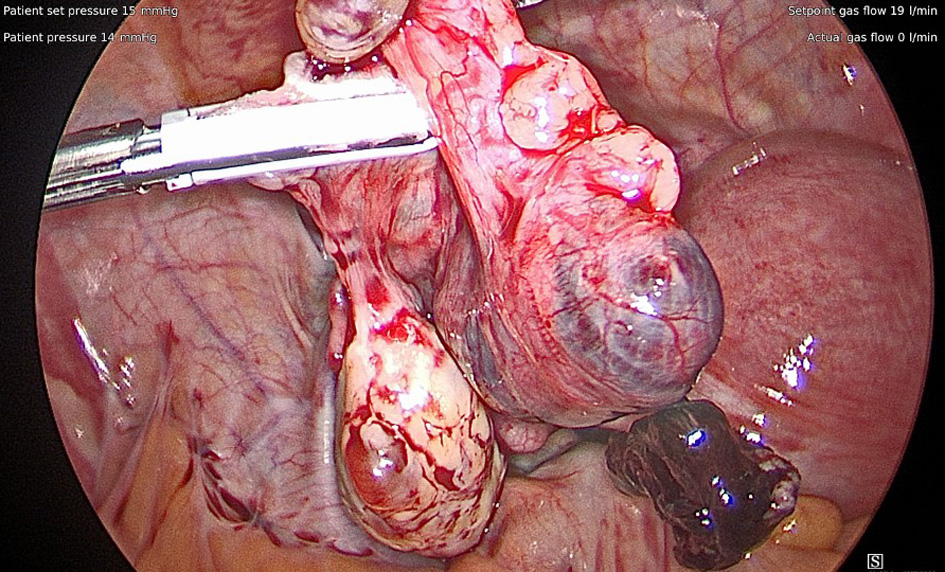 Click for large image | Figure 1. After clearing out the hemoperitoneum so the pelvis could be visualized, the left fallopian tube was noted to have what appeared to be a ruptured ectopic pregnancy. |
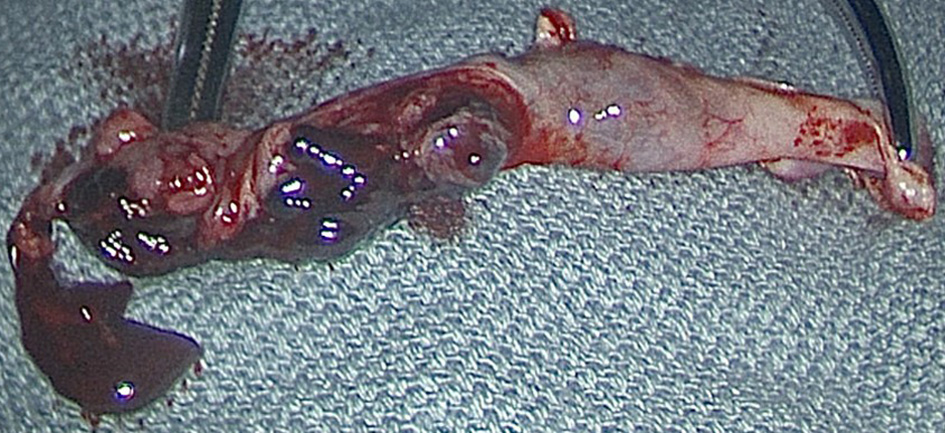 Click for large image | Figure 2. The left fallopian tube and ectopic pregnancy after salpingectomy. |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
Heterotopic pregnancy in natural conception cycles are rare and require a high index of suspicion for timely and accurate diagnosis in order to ensure proper management. Prior case reports have shown a variety of presentations for heterotopic pregnancies which include abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, adnexal mass, peritoneal irritation and an enlarged uterus [4-6]. Often symptoms are consistent with either an early IUP or an ectopic pregnancy, and thus a second pregnancy can be easily overlooked. Overlooking an extrauterine pregnancy places the patient at risk of tubal rupture and intraabdominal hemorrhage, while missing an IUP allows the patient to continue with an undiagnosed pregnancy and potential exposure to teratogens, particularly methotrexate if this is used to treat the ectopic pregnancy.
Ultrasound has been the primary modality for diagnosis of heterotopic pregnancy, but as this case demonstrates, this is not always a diagnosis feasible with imaging alone [1, 5, 7]. Blood, either in the uterine cavity or pelvis, can obscure visualization. Although both ovaries were visualized on the transvaginal ultrasound performed in the ED, it was difficult to assess the entire adnexa due to the burden of clot in the pelvis. Early transvaginal ultrasound to assess for pregnancy location and viability has been adopted in patients undergoing ART [1, 7, 8].
Regardless of the certainty (or uncertainty) of the diagnosis, it is crucial to provide expedient care for patients with hemoperitoneum who are showing signs of hemodynamic instability. Ignoring the clinical acuity of a patient due to ambiguity in a diagnosis puts the patient at risk of increased morbidity and mortality. Being prepared for a variety of findings and possible complications one may encounter upon surgical exploration allows for efficient and safe intraoperative management.
This particular case also highlights the importance of screening for pregnancy in reproductive aged females. Had a pregnancy test not been obtained upon initial presentation to the ED, this could have delayed her diagnosis further which potentially could have resulted in increased morbidity for the patient. For patients with a desired pregnancy, particularly those with infertility, they may wish to continue the IUP. Multiple case reports have demonstrated ongoing viable pregnancies and successful deliveries after treatment of the ectopic pregnancy in a heterotopic pregnancy, so this is a feasible option for them [3, 7, 8].
In conclusion, this rare case of a spontaneous heterotopic pregnancy illustrates the importance of keeping a broad differential diagnosis, including rare and potentially life-threatening etiologies. Postoperatively, multiple team members mentioned that a heterotopic pregnancy came to mind when thinking through the differential, but no one verbalized this as each person thought the diagnosis was too unlikely, even though it was consistent with the clinical picture. Although rare, heterotopic pregnancies do occur, and it is important to keep this in the differential for appropriate patients.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Rochester for the support in writing and submitting this case report.
Financial Disclosure
None of the authors have any financial disclosures.
Conflict of Interest
There are no potential competing or conflict of interest of a financial or other nature.
Informed Consent
The consent for publication of identifying material has been signed by the patient (who remains anonymous).
Author Contributions
All authors in this paper have met criteria for authorship. Drs. Samborski, Williams, and Spivack all contributed to the literature review, initial draft, and revisions. Dr. Gubbels contributed to the revisions for important content and for the final approval of the version that is being submitted.
Data Availability
Any inquiries regarding supporting data availability of this study should be directed to the corresponding author.
| References | ▴Top |
- Ludwig M, Kaisi M, Bauer O, Diedrich K. Heterotopic pregnancy in a spontaneous cycle: do not forget about it! Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1999;87(1):91-93.
doi - Rothman A, Shapiro J. Heterotopic pregnancy after homolateral salpingo-oophorectomy. Report of a case. Obstet Gynecol. 1965;26(5):718-720.
- Tal J, Haddad S, Gordon N, Timor-Tritsch I. Heterotopic pregnancy after ovulation induction and assisted reproductive technologies: a literature review from 1971 to 1993. Fertil Steril. 1996;66(1):1-12.
doi - Varras M, Akrivis C, Hadjopoulos G, Antoniou N. Heterotopic pregnancy in a natural conception cycle presenting with tubal rupture: a case report and review of the literature. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2003;106(1):79-82.
doi - Cheng PJ, Chueh HY, Qiu JT. Heterotopic pregnancy in a natural conception cycle presenting as hematometra. Obstet Gynecol. 2004;104(5 Pt 2):1195-1198.
doi pubmed - Gibson KR, Horne AW. Ruptured heterotopic pregnancy: an unusual presentation of an uncommon clinical problem. BMJ Case Rep. 2012;2012.
doi pubmed - Nabi U, Yousaf A, Ghaffar F, Sajid S, Ahmed MMH. Heterotopic pregnancy - a diagnostic challenge. Six case reports and literature review. Cureus. 2019;11(11):e6080.
doi - Guan Y, Ma C. Clinical outcomes of patients with heterotopic pregnancy after surgical treatment. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017;24(7):1111-1115.
doi pubmed
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Clinical Gynecology and Obstetrics is published by Elmer Press Inc.
