| Journal of Clinical Gynecology and Obstetrics, ISSN 1927-1271 print, 1927-128X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Gynecol Obstet and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jcgo.org |
Letter to the Editor
Volume 4, Number 2, June 2015, pages 235-236
Outcomes of Breastfeeding in Japanese Women With Flat or Inverted Nipples
Shunji Suzukia, b, Midori Kotakea, Asami Fujikawaa, Yukie Kasaharaa, Miyuki Nishikawaa, Yurina Wadaa, Sanae Kanaia
aDepartment of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Japanese Red Cross Katsushika Maternity Hospital, Tokyo, Japan
bCorresponding Author: Shunji Suzuki, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Japanese Red Cross Katsushika Maternity Hospital, 5-11-12 Tateishi, Katsushika-ku, Tokyo 124-0012, Japan
Manuscript accepted for publication February 02, 2015
Short title: Japanese Women With Flat Nipples
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.14740/jcgo307w
| To the Editor | ▴Top |
Occurrences of flat or inverted nipples are not uncommon problems and they often seriously hamper initiation and continuation of breastfeeding [1]. For example, these nipple problems may lead to a delay in breastfeeding initiation and thus deprive the baby from getting the benefits of colostrum. In addition, the inability to attach at the breast can cause infrequent suckling and it may lead to breast engorgement. If the mother is not shown how to maintain an adequate supply through expression of milk due to the problems, the production of milk is likely to decrease. In this study, we examined the prevalence of flat and inverted nipples among Japanese postpartum women and their influence on the rate of exclusive breastfeeding.
We reviewed the obstetric records of all healthy nulliparous women with vaginal or cesarean singleton deliveries at 37 - 41 weeks’ gestation at the Japanese Red Cross Katsushika Maternity Hospital between March 1 and October 31, 2014. In this study, the staffs those have been certified as an expert of breast care in our hospital checked every postpartum woman to define the nipple forms and the presence of inability to attach at the breast at 1 - 2 and 3 - 5 days after delivery, respectively. A face-to-face interview was conducted to ask about their feeding methods at 7 days and 1 month after delivery. In this study, we excluded cases of women receiving drugs contraindicated for those lactating, mothers with a habit of smoking and/or drinking, and mothers without partners because they have been already reported to be associated with the prevalence of exclusive breastfeeding in Japanese women [2]. Demographic information and the characteristics of labor such as the maternal age, neonatal birth weight, and delivery modes were extracted from patient charts.
For statistical analysis, the Χ2 test for categorical variables was used. Differences with P < 0.05 were considered significant.
Table 1 shows clinical characteristics and outcomes of breastfeeding during the study period. The rates of normal, flat and inverted nipples were 83.4%, 14.5% and 2.1%, respectively. There were no significant differences in these clinical characteristics among the three groups. The incidences of inability to attach at the breast in the women with flat and inverted nipples were significantly higher than that in the women with normal nipples (P < 0.01); however, there were no significant differences in the rate of exclusive breastfeeding at 7 days or 1 month after delivery among the three groups.
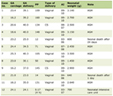 Click to view | Table 1. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Breastfeeding of Nulliparous Women With Vaginal or Cesarean Singleton Deliveries at 37 - 41 Weeks’ Gestation |
To date, some various therapies using instruments including rubber bands, breast shells, inverted syringes, or surgical corrections have been reported with varying success rates [1]; however, in our hospital we performed nipple exercise without any instruments. We have watch for the baby’s sucking to the mother’s nipple considering the necessity of minor modifications of the angle of the baby’s sticking. Therefore, the current results indicate the incidence nipple problems and the natural outcomes of their breastfeeding. The nipple problems may lead to the increased incidence of inability to attach at the breast; however, they may not lead to the decreased rate of exclusive breastfeeding.
| References | ▴Top |
- Chakrabarti K, Basu S. Management of flat or inverted nipples with simple rubber bands. Breastfeed Med. 2011;6(4):215-219.
doi pubmed - Kaneko A, Kaneita Y, Yokoyama E, Miyake T, Harano S, Suzuki K, Ibuka E, et al. Factors associated with exclusive breast-feeding in Japan: for activities to support child-rearing with breast-feeding. J Epidemiol. 2006;16(2):57-63.
doi pubmed
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Clinical Gynecology and Obstetrics is published by Elmer Press Inc.
