| Journal of Clinical Gynecology and Obstetrics, ISSN 1927-1271 print, 1927-128X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Gynecol Obstet and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.jcgo.org |
Case Report
Volume 9, Number 4, December 2020, pages 129-133
Rare Presentation of Fetus in Fetu - Laparoscopic Approach: A Case Report
Vandana Menona, c, Bedaya Amroa, Tasnim E.V. Kelothb, Arnaud Wattieza, Maan Hachmib
aLatifa Women and Children Hospital, Dubai, UAE
bDubai Hospital, Dubai, UAE
cCorresponding Author: Vandana Menon, Latifa Women and Children Hospital, Dubai, UAE
Manuscript submitted July 30, 2020, accepted October 12, 2020, published online December 15, 2020
Short title: Rare Presentation of FIF
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/jcgo681
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Fetus in fetu (FIF) is an extremely rare condition in which a malformed fetus is found most commonly in the abdomen of a living twin. We report a case of FIF in a young adult woman, which presented as a twisted ovarian cyst and was successfully managed by laparoscopy. This is the first reported case of FIF with an acute presentation, the first case in an adult ovary and the first to be managed successfully by laparoscopy. The excised ovarian mass was diagnosed as FIF with benign teratoma based on histopathological examination and radiography.
Keywords: Case report; Fetus in fetu; Dermoid; Laparoscopy; Abdominal mass
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Fetus in fetu (FIF) is a rare condition which usually presents as a vertebrate fetiform mass in a newborn or a child and occasionally in an adult man. It occurs in about 1 in 500,000 live births [1] and less than 200 cases have been reported in the medical literature. This is the third case in an adult female [2] and the first case managed by laparoscopy.
| Case Report | ▴Top |
We present the case of a 26-year-old nulliparous woman who attended our emergency department with acute, severe lower abdominal pain associated with vomiting. She did not have any relevant medical, gynecological or surgical history. She had an ultrasound in another facility which revealed a twisted multiloculated cyst of 11 × 7 cm size, most probably dermoid cyst.
Clinical examination revealed a tender abdomen with guarding. A firm mass of 16 cm size was palpable arising from the pelvis. A bedside ultrasound revealed a cyst of 16 cm with solid and cystic areas with significantly compromised vascularity. The tumour markers (beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)) were found to be normal. CA125 was slightly elevated at 78 U/mL (reference range: 0 - 35). Imaging modalities like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) could not be performed due to the severe pain at presentation and non-availability of MRI and CT in our facility. With a provisional diagnosis of twisted ovarian cyst, probably dermoid, we decided to perform emergency diagnostic laparoscopy and to proceed accordingly. Consent was taken for ovarian cystectomy and/or adnexectomy. Intraoperatively, the left ovary was found to be twisted six times around its pedicle with an ovarian cyst of 18 × 16 cm (Fig. 1) containing both solid and cystic areas. The whole ovary was grayish with a hemorrhagic surface, indicating ischemic changes. However, it had a smooth surface and had no suspicious features. Peritoneal fluid was aspirated for cytology. A systematic examination of the rest of the pelvis and upper abdomen was implemented and was found to be normal. The ovary was gently untwisted, after which it gradually started regaining its color. Taking into consideration the young age and nulliparity of the patient, ultrasound features of dermoid and no suspicious features of malignancy on inspection, we decided to go for laparoscopic cystectomy. After cyst aspiration, cystectomy was carried out in a large endo bag and the procedure was completed with minimal spillage of cheesy material. At extraction, a large bony part was felt significantly with sharp edges. So one lateral port was extended to 4 - 5 cm (Fig. 2) and cyst was completely extracted, which revealed a partly formed fetus. Reconstruction of the ovary was done with trimming of ovarian tissue and suturing using 2-0 poliglecaprone 25 (Ethicon Monocryl). Intraoperative blood loss was minimal (around 50 mL). The patient was discharged the next day with uneventful and fast recovery as expected from laparoscopic surgeries.
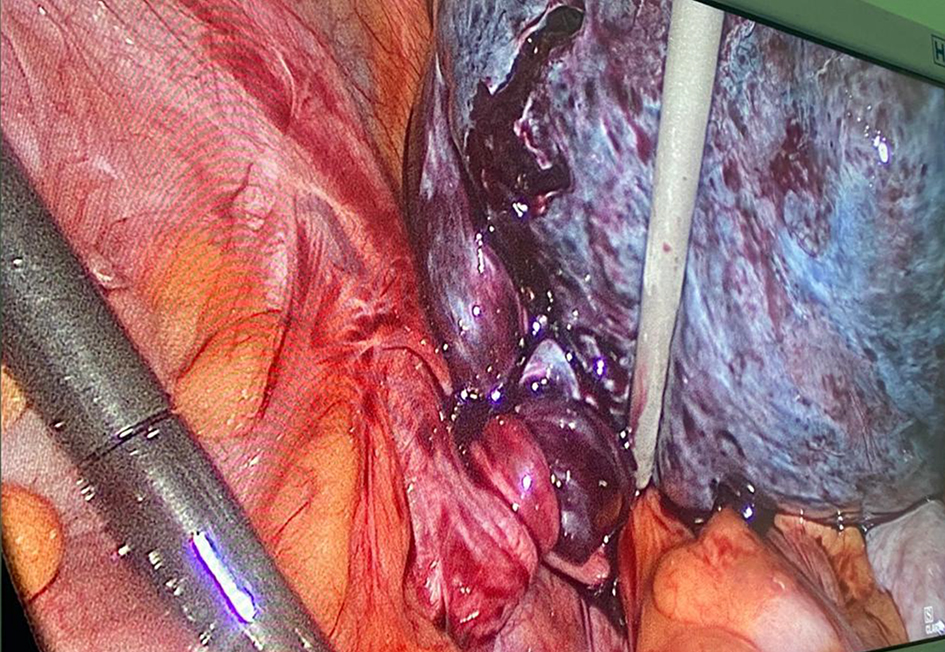 Click for large image | Figure 1. Intraoperative photograph showing twisted ovarian cyst. |
 Click for large image | Figure 2. Picture showing port positions on day 1 after laparoscopy. |
Gross specimen analysis, radiography and microscopic analysis in histopathology department were undertaken and a final diagnosis of FIF with teratoma was rendered. The presence of fetal skull, rudimentary limbs with digits, malformed trunk with vertebral column, gluteal region with central cleft and a polypoid structure resembling external genitalia support the FIF entity (Figs. 3-7).
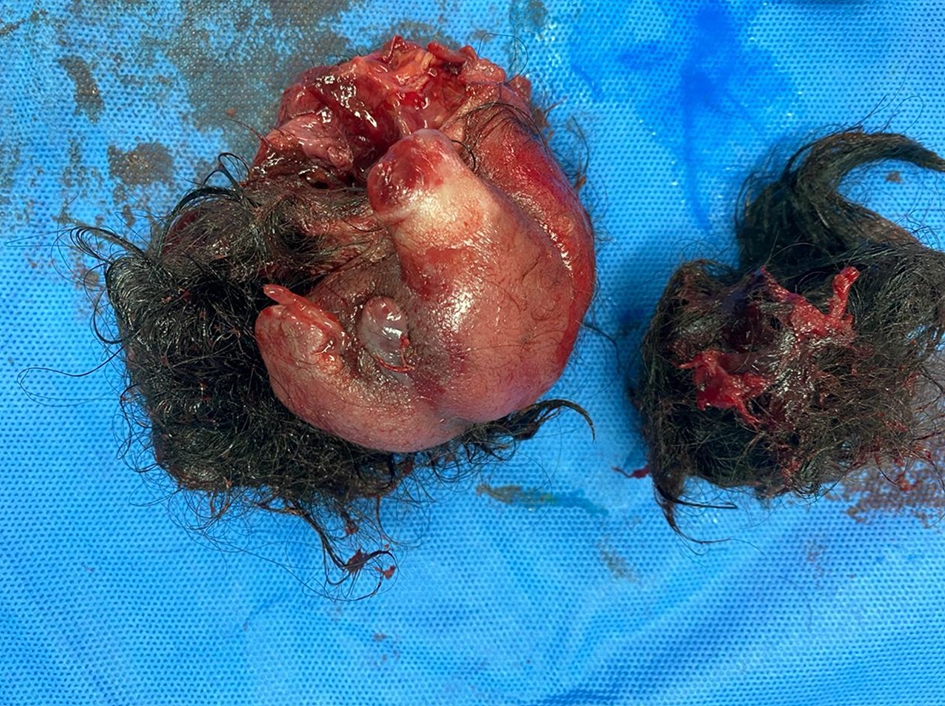 Click for large image | Figure 3. Gross photograph of content of ovarian cyst after extraction. Rudimentary fetus weighed 216 g, covered with skin, showing gluteal cleft, both lower limb buds and ill-developed external genitalia. |
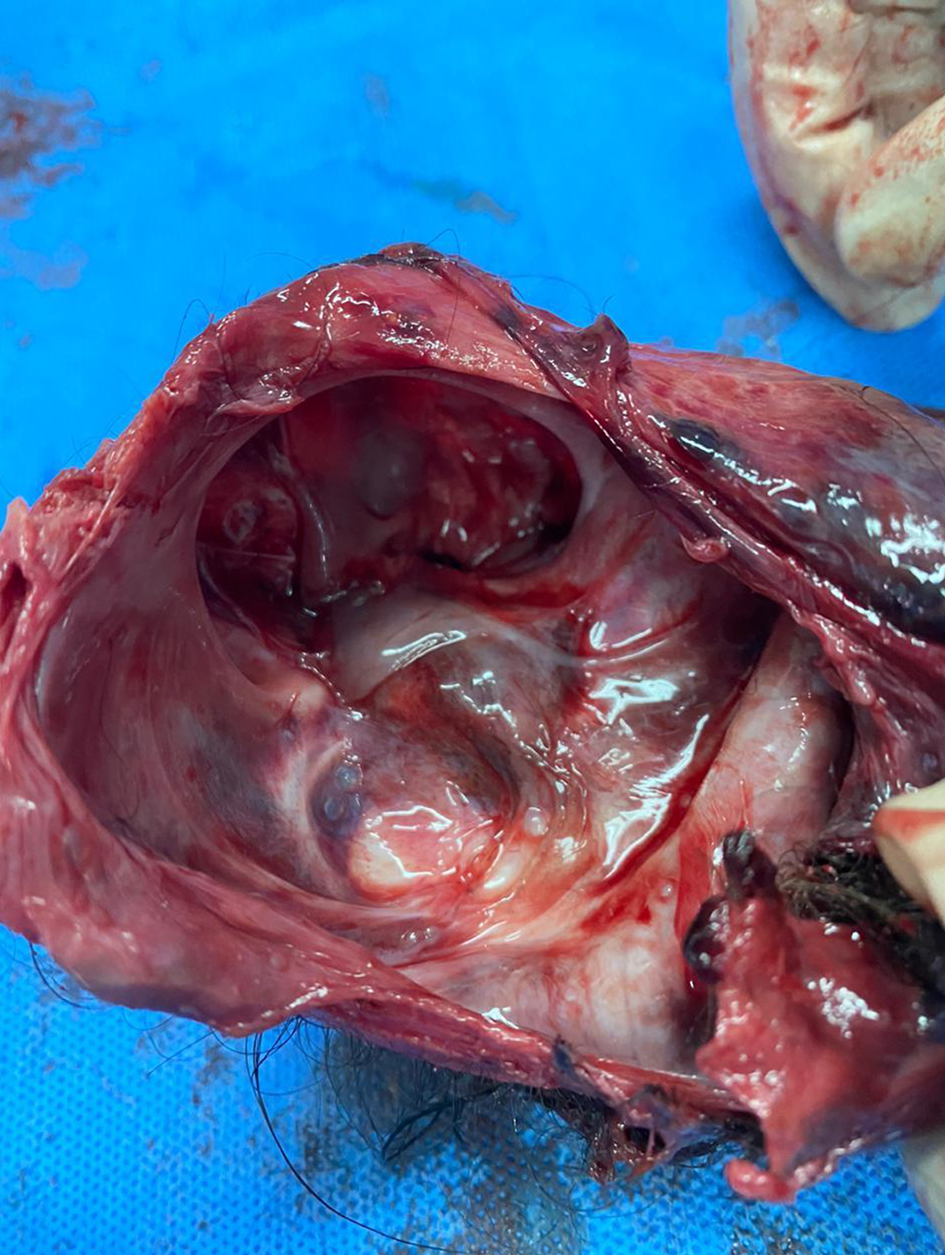 Click for large image | Figure 4. Gross photograph of skull in rudimentary fetus. |
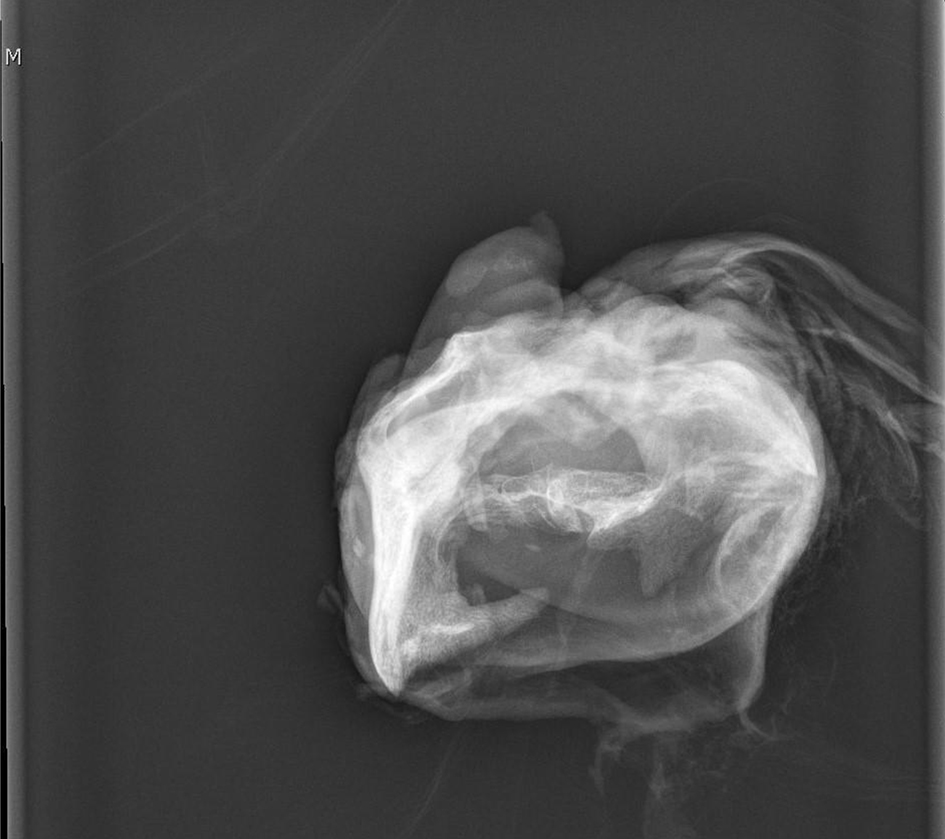 Click for large image | Figure 5. Plain X-ray showing embryonic vertebral column and long bones corresponding to fetal limbs. |
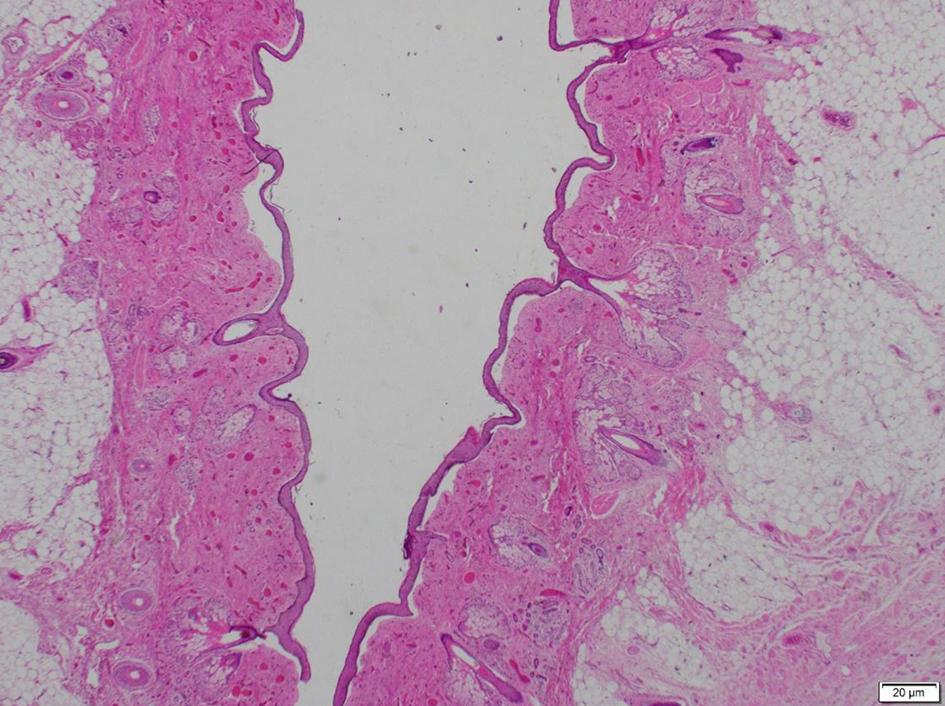 Click for large image | Figure 6. Photomicrograph showing skin, hair follicles and adnexal appendages. |
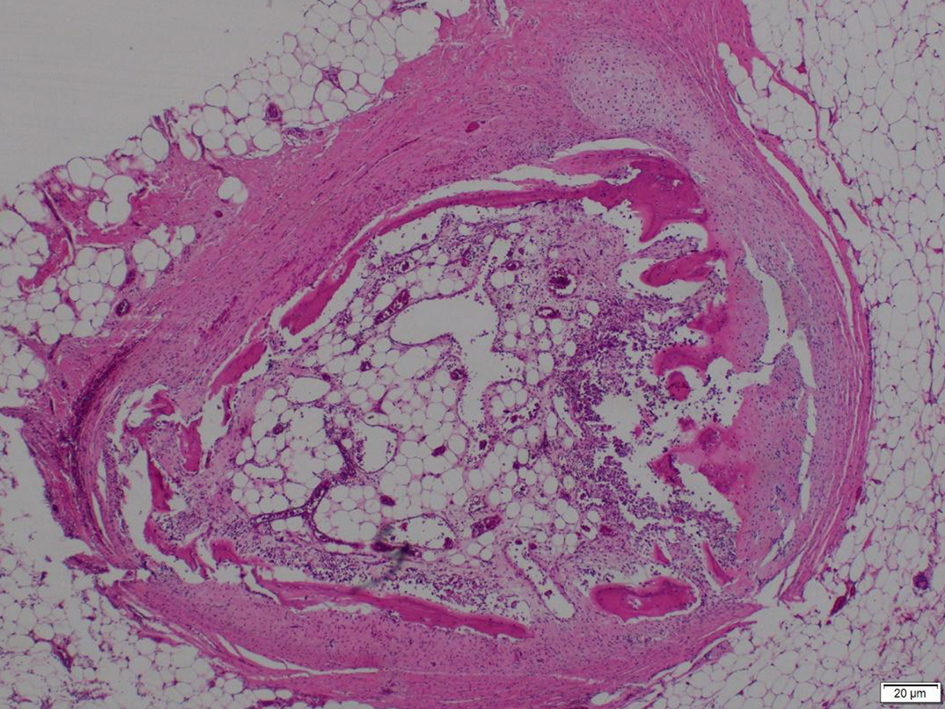 Click for large image | Figure 7. Photomicrograph showing cartilage, bone and bone marrow elements and fibroadipose tissue. |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
The present case is the ninth reported case of adult FIF (89% occurring before 18 months) and the third case in an adult female (Table 1) [2-9]. To our knowledge, this is the only known case of FIF reported in an adult ovary. Furthermore, this is the only reported case which has been managed laparoscopically and an acute presentation has so far not been described. Although benign, malignant recurrence has been recorded with FIF [10].
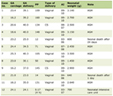 Click to view | Table 1. Reported Cases of Adult FIF and Their Characteristics Between 1992 and 2019 [2-9] |
The term FIF was first described by Friedrich Meckel. There is controversy as to whether this is a distinct entity or a highly organised teratoma. The most accepted theory is the twin theory which states that FIF is a monochorionic, diamniotic twin which becomes incorporated in the body of host twin after anastomosis of vitelline circulation [11]. According to Willis in 1953, identification of vertebral column ensures the diagnosis of FIF and differentiates this from teratoma. Identification of vertebral column indicates that fetal evolution must have advanced at least to a primitive streak stage to develop notochord [12]. Some investigators like Prescher et al hypothesized that FIF represents a well-differentiated and highly organized teratoma [13]. Our case supports the twin theory of origin of FIF due to the high level of organization of tissues and not a cluster of primitive tissues.
The common presentation of FIF is a mass in the abdomen, almost 80% in the retroperitoneum [2], although it has been reported at various sites right from the cranial cavity to the scrotum. Different organs can be seen in FIF, including vertebral column (91%), limbs (82.5%), central nervous system (55.8%), gastrointestinal tract (45%), vessels (40%) and genitourinary tract (26.5%) [14]. The mass may compress the surrounding organs leading to symptoms such as abdominal distension, feeding difficulty, vomiting, jaundice or pressure effects on the renal or respiratory system. A presumptive diagnosis can be made by ultrasound, plain radiography, CT scan or MRI which will reveal the presence of axial skeleton and vertebral column. Nevertheless, this should not lead to diagnostic exclusion as an underdeveloped spinal column may not be visualized by radiography [15]. Molecular analysis using a genetic marker for uniparental isodisomy of chromosomes 14 and 15 has been described [16]. Treatment of FIF is surgical. Although majority of the cases are benign, complete excision of FIF together with the capsule is crucial as malignant recurrence has been reported rarely, especially if part of the tissue is not completely excised [10]. A few authors have advocated follow-up for tumor recurrence using tumor markers like AFP, with some of them suggesting 2 years as the ideal time frame, especially when FIF and teratoma are considered as part of the same spectrum [13].
Conclusions
Although FIF is a rare entity with a chronic course, the possibility should be kept in mind while dealing with an emergency like a twisted ovarian cyst, in spite of the unusual location and sex predilection. The operation to remove FIF can be challenging if the mass is highly vascular with multiple feeding vessels and has been traditionally performed by laparotomy. The aforementioned case proves that laparoscopy is a feasible option in the management of FIF and other partly solid adnexal masses in expert hands. Postoperative follow-up with screening using tumor markers, especially AFP is mandatory if initial levels are raised to rule out malignant recurrence.
Acknowledgments
None to declare.
Financial Disclosure
None to declare.
Conflict of Interest
None to declare.
Informed Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report.
Author Contributions
Vandana Menon performed surgery and postoperative follow-up, and manuscript preparation. Bedaya Amro performed surgery and manuscript preparation. Tasnim E. V. Keloth contributed to histopathology examination and manuscript preparation. Arnaud Wattiez contributed to manuscript supervision. Maan Haachmi contributed to radiology examination and diagnosis.
Data Availability
The authors declare that data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
| References | ▴Top |
- Grant P, Pearn JH. Foetus-in-foetu. Med J Aust. 1969;1(20):1016-1019.
doi pubmed - Kumar A, Paswan SS, Kumar B, Kumar P. Fetus in fetu in an adult woman. BMJ Case Rep. 2019;12(8):e230835.
doi pubmed - Shrivastava SK, Sharma HP, Sinha SK, Prasad KM. Retroperitoneal, teratoma as fetus in fetu—a case report. Indian Journal of Pathology & Microbiology. 1999;42(2):169-170.
- Dagradi AD, Mangiante GL, Serio GE, Musajo FG, Menestrina FV. Fetus in fetu removal in a 47-year-old man. Surgery. 1992;112(3):598-602.
- Awasthi M, Narlawar R, Hira P, Shah P. Fetus in fetu. Rare cause of a lump in an adult's abdomen. Australas Radiol. 2001;45(3):354-356.
doi pubmed - Massad MG, Kong L, Benedetti E, Resnick D, Ghosh L, Geha AS, Abcarian H. Dysphagia caused by a fetus-in-fetu in a 27-year-old man. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001;71(4):1338-1341.
doi - Murtaza A, Kanhaiya C, Sadhna M, Sabiha M. Fetus in fetu: a rare presentation in an adult female. Oman Med J. 2010;25.
doi - Sharma N, Verma P, Pathak P. 27 cm fetus in fetu presenting in a 36-year-old man: report of a rare case and brief review of literature. Indian J Surg. 2007;69(4):155-157.
doi pubmed - Daga BV, Chaudhary VA, Ingle AS, Dhamangaokar VB, Jadhav DP, Kulkarni PA. Double fetus-in-fetu: CT scan diagnosis in an adult. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2009;19(3):216-218.
doi pubmed - Hopkins KL, Dickson PK, Ball TI, Ricketts RR, O'Shea PA, Abramowsky CR. Fetus-in-fetu with malignant recurrence. J Pediatr Surg. 1997;32(10):1476-1479.
doi - Spencer R. Parasitic conjoined twins: external, internal (fetuses in fetu and teratomas), and detached (acardiacs). Clin Anat. 2001;14(6):428-444.
doi pubmed - Willis RA. The borderland of embryology and pathology. 2nd edn. Washington, DC: Butterworths. 1962:44.
- Prescher LM, Butler WJ, Vachon TA, et al. Fetus in fetu: Review of the literature over the past 15 years. J Pediatr Surg Case Rep. 2015;3:554-562.
doi - Ji Y, Chen S, Zhong L, Jiang X, Jin S, Kong F, Wang Q, et al. Fetus in fetu: two case reports and literature review. BMC Pediatr. 2014;14:88.
doi pubmed - Hoeffel CC, Nguyen KQ, Phan HT, Truong NH, Nguyen TS, Tran TT, Fornes P. Fetus in fetu: a case report and literature review. Pediatrics. 2000;105(6):1335-1344.
doi pubmed - Miura S, Miura K, Yamamoto T, Yamanaka M, Saito K, Hirabuki T, Kurosawa K, et al. Origin and mechanisms of formation of fetus-in-fetu: two cases with genotype and methylation analyses. Am J Med Genet A. 2006;140(16):1737-1743.
doi pubmed
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Clinical Gynecology and Obstetrics is published by Elmer Press Inc.
