| Journal of Clinical Gynecology and Obstetrics, ISSN 1927-1271 print, 1927-128X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Gynecol Obstet and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jcgo.org |
Case Report
Volume 7, Number 1, March 2018, pages 26-29
Case Report of a Primary Ovarian Leiomyosarcoma Diagnosed by H-Caldesmon Staining
Asuka Tanakaa, b, Ai Miyoshia, Serika Kanaoa, Masumi Takedaa, Mayuko Mimuraa, Masaaki Nagamatsua, Takeshi Yokoia
aDepartment of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Kaizuka City Hospital, Kaizuka, Osaka, Japan
bCorresponding Author: Asuka Tanaka, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Kaizuka City Hospital, 3-10-20 Hori Kaizuka, Osaka 597-0015, Japan
Manuscript submitted January 18, 2018, accepted March 8, 2018
Short title: Ovarian Leiomyosarcoma and H-Caldesmon Positive
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/jcgo477w
| Abstract | ▴Top |
The patient was 64-year-old female who presented with complaints of a lower abdominal mass. A total abdominal hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, pelvic lymphadenectomy and omentectomy were performed. Histological findings of a characteristic arrangement of spindle-shaped cells and diffusively positive immunohistochemical staining for h-caldesmon confirmed a pathological diagnosis of left ovarian leiomyosarcoma.
Keywords: Ovarian leiomyosarcoma; H-caldesmon; Immunohistochemical staining
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Primary ovarian leiomyosarcoma is relatively rare, representing less than 2-3% of all malignant ovarian tumors [1, 2], with some reports giving its incidence as less than 0.1% [3, 4]. Only 72 cases have been reported in the English literature [5]. Due to their rare occurrence, the diagnosis is often difficult, and there is currently no established standard treatment for ovarian leiomyosarcomas. We describe herein our experience with such rare case of primary ovarian leiomyosarcoma, to help others in understanding its diagnosis by h-caldesmon staining.
| Case Report | ▴Top |
The patient was a 64-year-old female (gravida 1, para 1). There was no particular personal or family medical history. She presented with complaints of 3 months of incontinence and a lower abdominal mass. She consulted her gynecologist and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed a solid mass of 15 cm in diameter, with some cystic portions, in her pelvis. With a suspicion of a malignant tumor, she has consulted to our hospital.
On admission, the patient was found to have a hard tumor in her lower abdomen; its mobility was poor. She did not feel tenderness at the tumor site. Abdominal ultrasonography revealed a solid tumor having a clear boundary but an irregular shape. Cytological diagnosis of the uterine cervix revealed NILM. Her serum levels of CA125 (≤ 35 U/mL), CA19-9 (≤ 37 U/mL) and CEA (≤ 5 ng/mL) were within normal range. LDH was modestly increased to 244 IU/L (LDH-1: 19 IU/L, LDH-2: 33 IU/L, LDH-3: 25 IU/L, LDH-4: 11 IU/L, LDH-5: 2 IU/L). Computed tomography (CT) revealed a solid soft-tissue tumor, approximately 15 cm in diameter, having an irregular shape and contrast enhancement (Fig. 1).
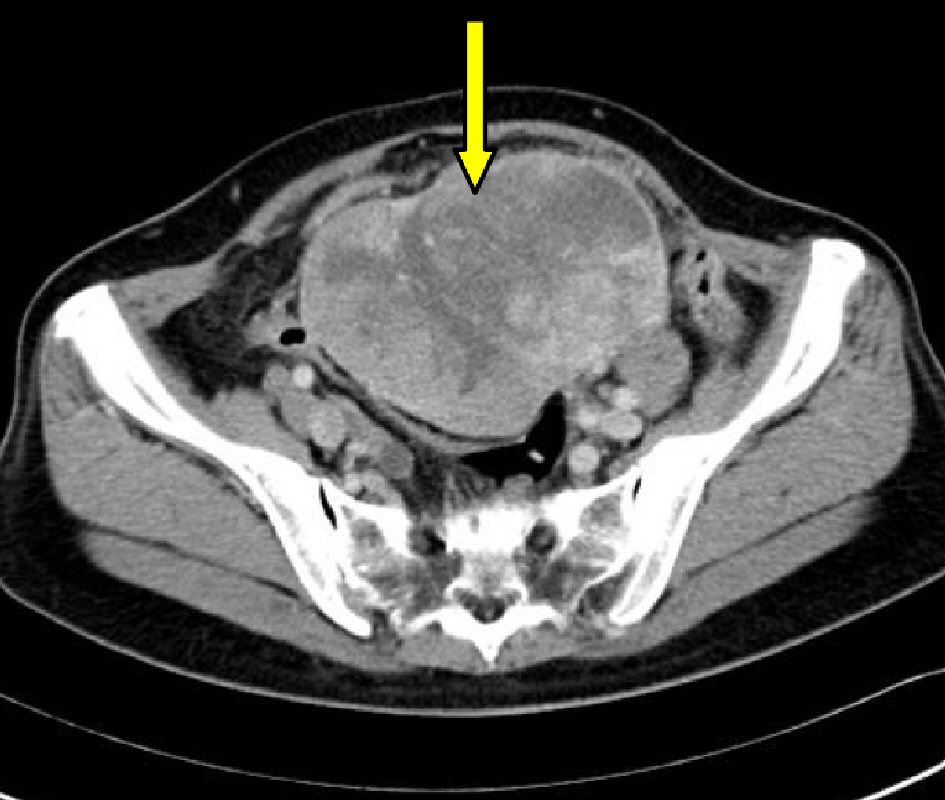 Click for large image | Figure 1. Pelvic computed tomography image: a large mass (arrow) occupying the pelvis, with an irregular shape and contrast enhancement is shown. |
We performed a laparotomy for the resection of abdominal mass, and for confirmation of the tumor pathology. The size of the uterus was normal; no abnormality was observed in the right ovary. The tumor was found to have developed from the left ovary and was completely separated from the uterus. There was adhesion between the tumor and mesenterium, however, direct invasion to neighboring organs were not found. There was a small amount of ascites, the cytodiagnosis of which was negative. While the tumor was being detached from the mesenterium, the tumor had collapsed. As the intraoperative pathological diagnosis of the tumor was a fibrosarcoma, we additionally performed a total abdominal hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, pelvic lymphadenectomy and omentectomy. We decided to refrain the procedure of aortic lymphadenectomy, because the intraoperative diagnosis indicated that the tumor showed a low potential of malignancy, considering the surgical invasion for the patient.
The tumor was an elastic hard solid mass 17cm in diameter (white, tinged with yellow), with an irregular surface (Fig. 2). The histological findings with H&E staining revealed spindle-shaped tumor cells (with relatively uniform oval or spindle-shaped nuclei), arranged in complicated fascicles (Fig. 3). Nuclear mitoses were seen in more than 20 cells per 10 high-power fields (Fig. 4). Various sizes of well-defined coagulated and necrotic tissue were seen within the tumor (Fig. 5).
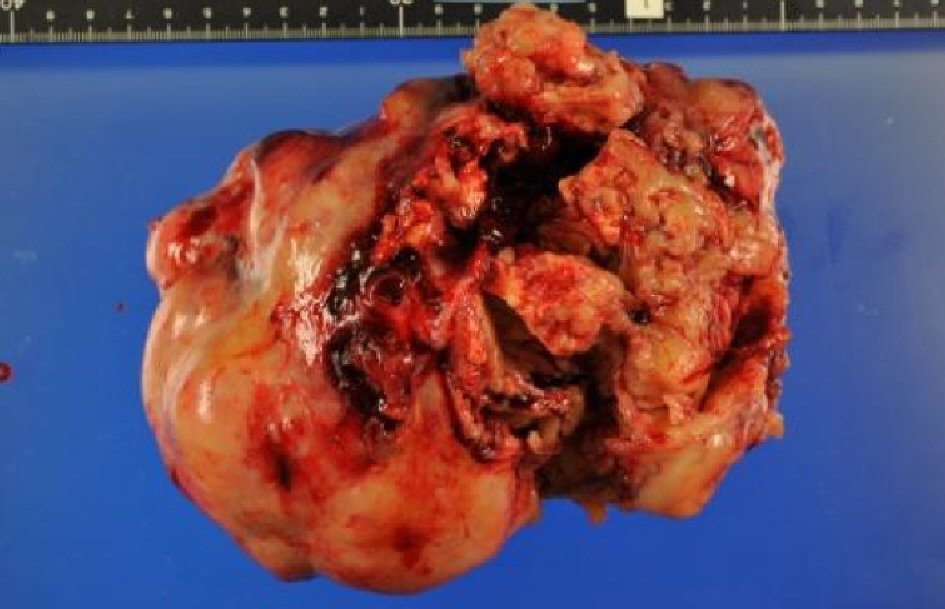 Click for large image | Figure 2. Macro findings of left ovarian tumor: an elastic hard yellow tumor with an uneven surface, 17 cm in diameter is shown. |
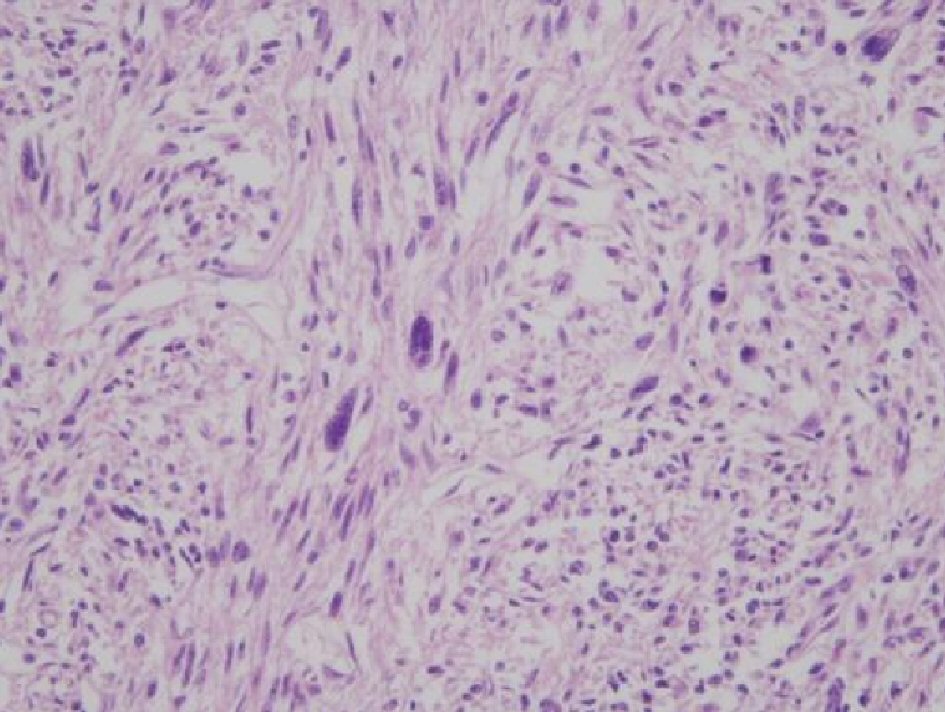 Click for large image | Figure 3. Microscopic findings of ovarian tumor (H&E, × 200): spindle-shaped tumor cells arranged in complicated fascicles, with relatively uniform oval and spindle-shaped nuclei are shown. |
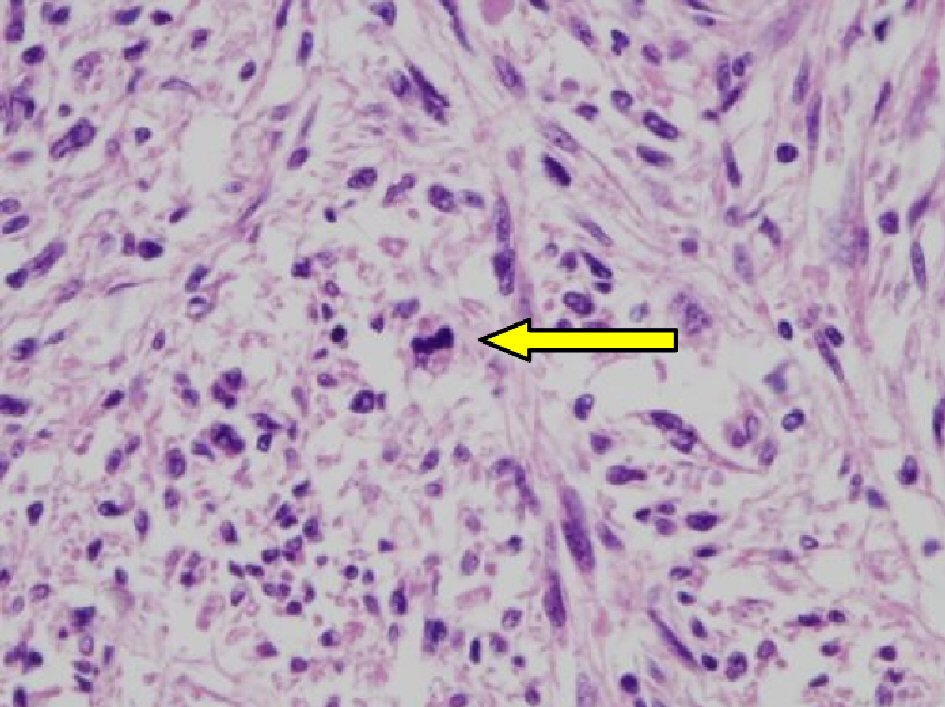 Click for large image | Figure 4. Microscopic findings of ovarian tumor showing abnormal nuclear mitosis (H&E, × 400): Scattered mitosis was seen within the tumor (arrow). The number of mitoses was counted as more than 20 per 10 high-power fields. |
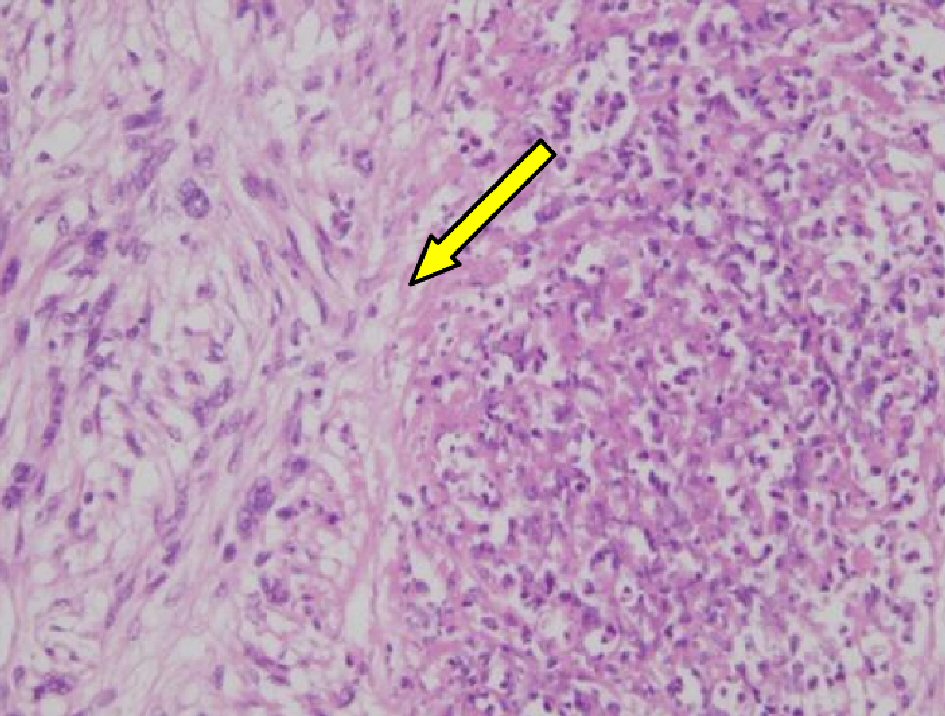 Click for large image | Figure 5. Microscopic findings of ovarian tumor (H&E, × 200): well-defined coagulated and necrotic tissues (arrow) with various sizes are noted in the tumor. |
Immunohistochemical staining demonstrated that the tumor was strongly positive for vimentin, a common mesenchymal marker. However, the tumor showed no reactivity with desmin and α-SMA, which are often expressed in tumors arising from smooth muscle, and S-100 was slightly positive. Based on these histological findings, we at first diagnosed the tumor as a malignant peripheral sheath tumor. However, malignant peripheral sheath tumors arising from the ovary are extremely rare, we consulted a pathologist specialized in gynecology and we additionally carry out h-caldesmon staining. The staining revealed that most of the neoplastic cells were strongly positive for h-caldesmon (Fig. 6). We performed S-100 staining again, but it turned out negative on this repeat. The tumor was also negative for CD34, EMA, calretinin, and c-kit (figure not shown).
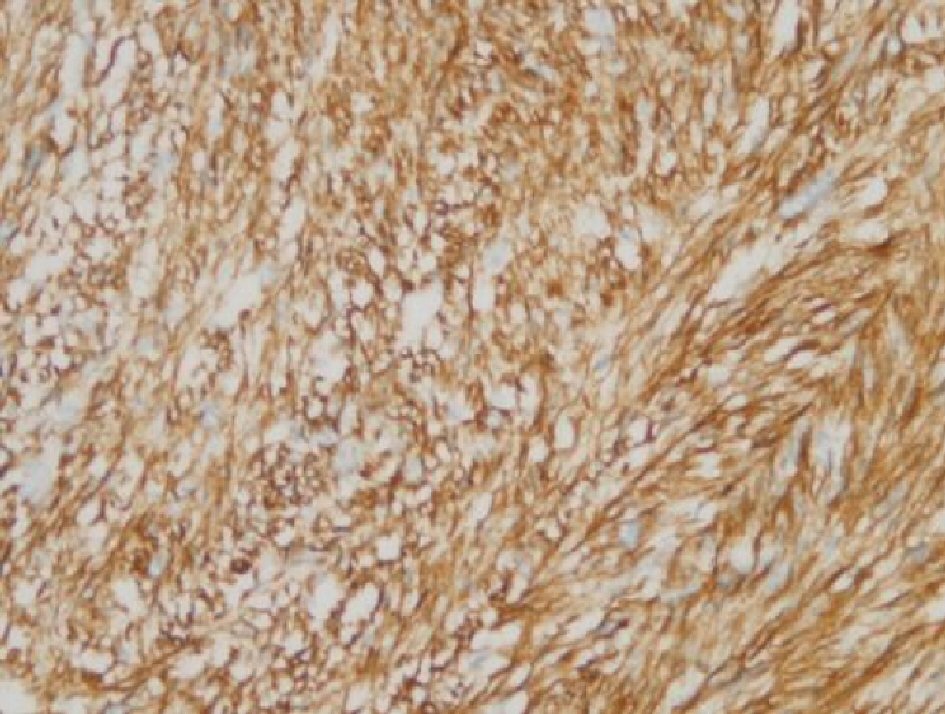 Click for large image | Figure 6. Immunohistochemical staining for h-caldesmon: the tumor cytoplasm was strongly positive for h-caldesmon. |
With these histological findings, particularly with the spindle-shaped cells and their specific arrangement, and with the immunohistochemical staining results, in particular, the tumor cells diffusively positive for h-caldesmon, we conclusively diagnosed the tumor as an ovarian leiomyosarcoma. Our final diagnosis was of a primary left ovarian leiomyosarcoma, pT1c2N0M0, stage IC2.
As there is no established treatment modality for this rare type of tumor, following discussions with the patient and her family, we decided to forego adjuvant therapy and to proceed with only outpatient-clinic follow-up. No signs of recurrence were found during the first 16 months after the operation. At 17 months of follow-up, the abdominal CT found a mass 5cm in maximum diameter above the vaginal stump, with swelling of the para vena caval lymph nodes. Her serum LDH was slightly increased, to 256 IU/L.
She was diagnosed as a recurrence of ovarian leiomyosarcoma. She was planned for treatment with six cycles of combination chemotherapy with gemcitabine hydrochloride and docetaxel hydrate, given intravenously at 3-week intervals. After five cycles, the patient complained respiratory discomfort. Examination by thoracic CT revealed interstitial pneumonia that was presumed to be due to the gemcitabine hydrochloride. Although the mass above the vaginal stump had been reduced to 2.5 cm in diameter, and rectal vaginal fistula was suspected due to rectal infiltration of the cancer. We decided to discontinue the chemotherapy because of the adverse drug reaction. Worrying about the exacerbating the rectal vaginal fistula due to radiotherapy (RT) for pelvic tumor, the patient did not wish to receive RT. Hence, we followed her on an outpatient-clinic basis.
At 8 months after her last chemotherapy, the mass above the vaginal stump was found to have increased to 3.3 cm in maximum diameter. We planned additional combination chemotherapy, this time with paclitaxel and carboplatin, given intravenously at 3-week intervals. After three cycles, our evaluation of her response to the treatment was that of a progressive disease. The patient hoped to receive only the best supportive care. Thirty-five months after the initial surgery, the patient had accumulated massive amounts of pleural effusion. She received terminal supportive care until her death.
| Discussion | ▴Top |
Primary ovarian sarcomas are relatively rare; the reported incidence varies from 0.1% to 3% of all malignant ovarian tumors [1-4]. Primary leiomyosarcoma of the ovary usually affects post-menopausal women, as was the case with the present report, with the average age of onset reported to be 53 years old. Symptoms such as lower abdominal pain and lower abdominal mass are common, however, most cases are asymptomatic in early stage, and are diagnosed at advanced stages [2].
Histologically, the ovarian leiomyosarcoma is characterized as spindle-shaped tumor cells arranged in a whorled pattern, with areas of nuclear mitosis and necrosis [6]. For the differential diagnosis of ovarian leiomyosarcoma from other spindle-cell tumors, such as a fibrosarcoma or fibroma, immunohistochemical staining is reported to be useful [6]. Muscle-specific actin, desmin, vimentin, and p53 immunohistochemical staining are effective discrimination factors [7]. However, in the present case, there was no reactivity with desmin or α-SMA, which is often expressed in tumors arising from smooth muscle, which implies that the tumor did not have myogenic origin. The tumor was strongly positive for vimentin and h-caldesmon, which are also common markers for mesenchymal neoplastic cells [8, 9]. Particularly, h-caldesmon, which is cytoskeleton-associated actin-binding protein, has been reported to be more specific myogenic markers. There is a study which examined 72 tumors, and diffuse staining for h-caldesmon was present only within the leiomyosarcomas [10]. For the detection of smooth muscle differentiation, even if desmin or α-SMA is immunohistochemically negative, h-caldesmon is considered to be another reliable marker. With these pathological and immunohistochemical results, we were able to reach the final diagnosis of primary ovarian leiomyosarcoma.
Due to the rarity of the disease, there is currently no established standard treatment for ovarian leiomyosarcomas. The main treatment is surgery, consisting of total abdominal hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, and excision of the residual tumor for debulking, if a total tumor resection is possible [2, 11].
To increase the survival rate for patients with leiomyosarcoma of the ovary, it might necessitate surgery and radiotherapy, combined with chemotherapy and immunotherapy treatments to destroy distant metastases. Surgical procedures have been shown to provide symptomatic relief from the lower abdominal pain. Although chemotherapy and radiation therapy have been used in the adjuvant setting, they have not been proven to have additional benefits [12]. We have tried to use a similar chemotherapy regimen with uterine leiomyosarcoma or ovarian cancer, for the recurrent disease in present case. The tumor was partially responded to combination of gemcitabine hydrochloride and docetaxel hydrate, although, the adverse effect of interstitial pneumonia forced us to halt the treatment
Conclusions
Primary ovarian sarcomas are so rare that we sometimes have difficulty in diagnosis. In present case, we at first have diagnosed the ovarian tumor as a malignant peripheral sheath tumor, although, histological findings of the spindle-shaped cells and their specific arrangement also seemed to indicate leiomyosarcoma. When leiomyosarcoma can be taken into consideration as a differential diagnosis, immunohistochemical staining, particularly h-caldesmon might be useful for accurate diagnosis, giving more reliable information of smooth muscle differentiation.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Buzard GS for his editing of the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
None declared.
Financial Support
There was no funding source for this research.
Declaration
These findings will be presented at the 50th Annual Meeting of the Japan Society of Clinical Oncology in Yokohama, Japan, April 25 to 27, 2017.
Funding
Funded for editing by Kaizuka City Hospital.
| References | ▴Top |
- Shakfeh SM, Woodruff JD. Primary ovarian sarcomas: report of 46 cases and review of the literature. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1987;42(6):331-349.
doi - Bouie SM, Cracchiolo B, Heller D. Epithelioid leiomyosarcoma of the ovary. Gynecol Oncol. 2005;97(2):697-699.
doi pubmed - Cortes J, Cuartero ML, Rossello JJ, Torrecabota J, Yarnoz MC, Llompart M. Ovarian pure leiomyosarcoma: case report. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 1987;8(1):19-22.
pubmed - Anderson PW, Macaulay L, Do YS, Sherrod A, d’Ablaing G, Koss M, Shinagawa T, et al. Extrarenal renin-secreting tumors: insights into hypertension and ovarian renin production. Medicine (Baltimore). 1989;68(5):257-268.
doi - He M, Deng YJ, Zhao DY, Zhang Y, Wu T. Synchronous leiomyosarcoma and fibroma in a single ovary: A case report and review of the literature. Oncol Lett. 2016;11(4):2510-2514.
doi pubmed - Friedman HD, Mazur MT. Primary ovarian leiomyosarcoma. An immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1991;115(9):941-945.
pubmed - Balaton A, Vaury P, Imbert MC, Mussy MA. Primary leiomyosarcoma of the ovary: a histological and immunocytochemical study. Gynecol Oncol. 1987;28(1):116-120.
doi - Lopez-Ruiz ME, Yebenes L, Berjon A, Hardisson D. Primary leiomyosarcoma of the ovarian vein: case report and literature review. Int J Surg Pathol. 2017;25(4):339-343.
doi pubmed - Chang A, Schuetze SM, Conrad EU, 3rd, Swisshelm KL, Norwood TH, Rubin BP. So-called “inflammatory leiomyosarcoma”: a series of 3 cases providing additional insights into a rare entity. Int J Surg Pathol. 2005;13(2):185-195.
doi pubmed - Ceballos KM, Nielsen GP, Selig MK, O’Connell JX. Is anti-h-caldesmon useful for distinguishing smooth muscle and myofibroblastic tumors? An immunohistochemical study. Am J Clin Pathol. 2000;114(5):746-753.
doi pubmed - Dixit S, Singhal S, Baboo HA, Vyas RK, Neema JP, Murthy R, Sooryanaraya U. Leiomyosarcoma of the ovary. J Postgrad Med. 1993;39(3):151-153.
pubmed - Taskin S, Taskin EA, Uzum N, Ataoglu O, Ortac F. Primary ovarian leiomyosarcoma: a review of the clinical and immunohistochemical features of the rare tumor. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2007;62(7):480-486.
doi pubmed
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Clinical Gynecology and Obstetrics is published by Elmer Press Inc.
